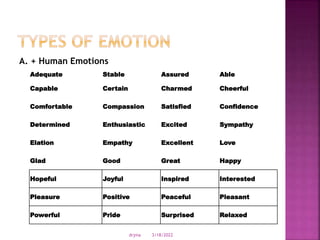
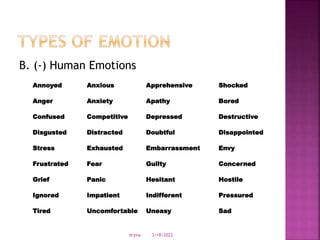
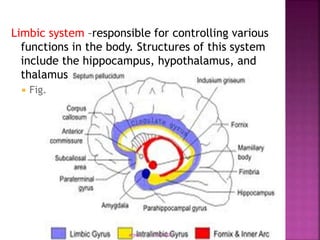
The document discusses various theories of emotion. It describes somatic theories which claim that bodily responses are essential to emotions. The James-Lange theory argues that emotional experience is due to bodily changes. Cognitive theories view emotions as involving cognitive appraisals and judgments. Neurobiological theories see emotions arising from structures in the limbic system of the brain like the hippocampus and hypothalamus. Situated perspectives view emotions as influenced by one's environment and observations of others.





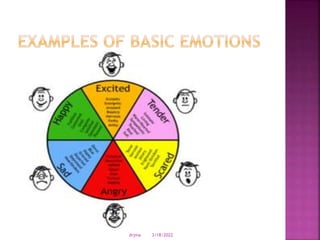
![ Cognitive" versus "non-cognitive" emotions [2]
Instinctual emotions (from the amygdala),
versus cognitive emotions (from the
prefrontal cortex)
Universal emotions recognized cross-
culturally based on research on identification
of facial expressions
3/18/2022
drjma](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emotion-drjma-130215074350-phpapp01/85/Emotion-drjma-8-320.jpg)