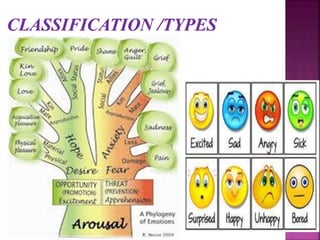
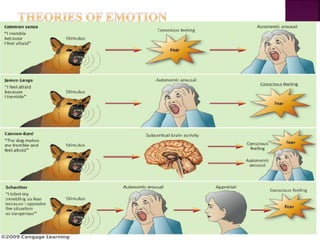
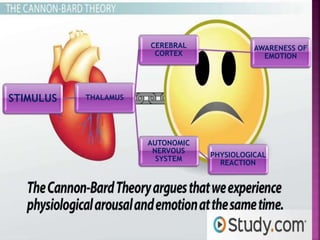
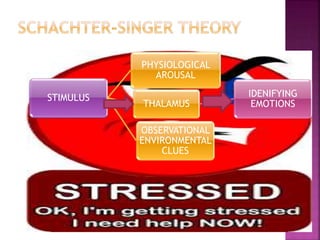
Emotions are complex states that involve physiological, cognitive, and behavioral components. They arise from our interpretation of situations based on physiological arousal and environmental cues. The three main theories on emotions are the James-Lange theory, which claims physiological arousal precedes emotions, the Cannon-Bard theory, which says physiological arousal and emotional experience occur simultaneously, and the Schachter-Singer theory, which posits that physiological arousal and cognitive labeling of the situation together produce distinct emotions. Emotions are expressed through facial expressions, vocal tones, and body language and involve physiological changes in the body. People can learn to control emotions using biofeedback, drugs, desensitization, flooding, self-statements, and coping strategies.