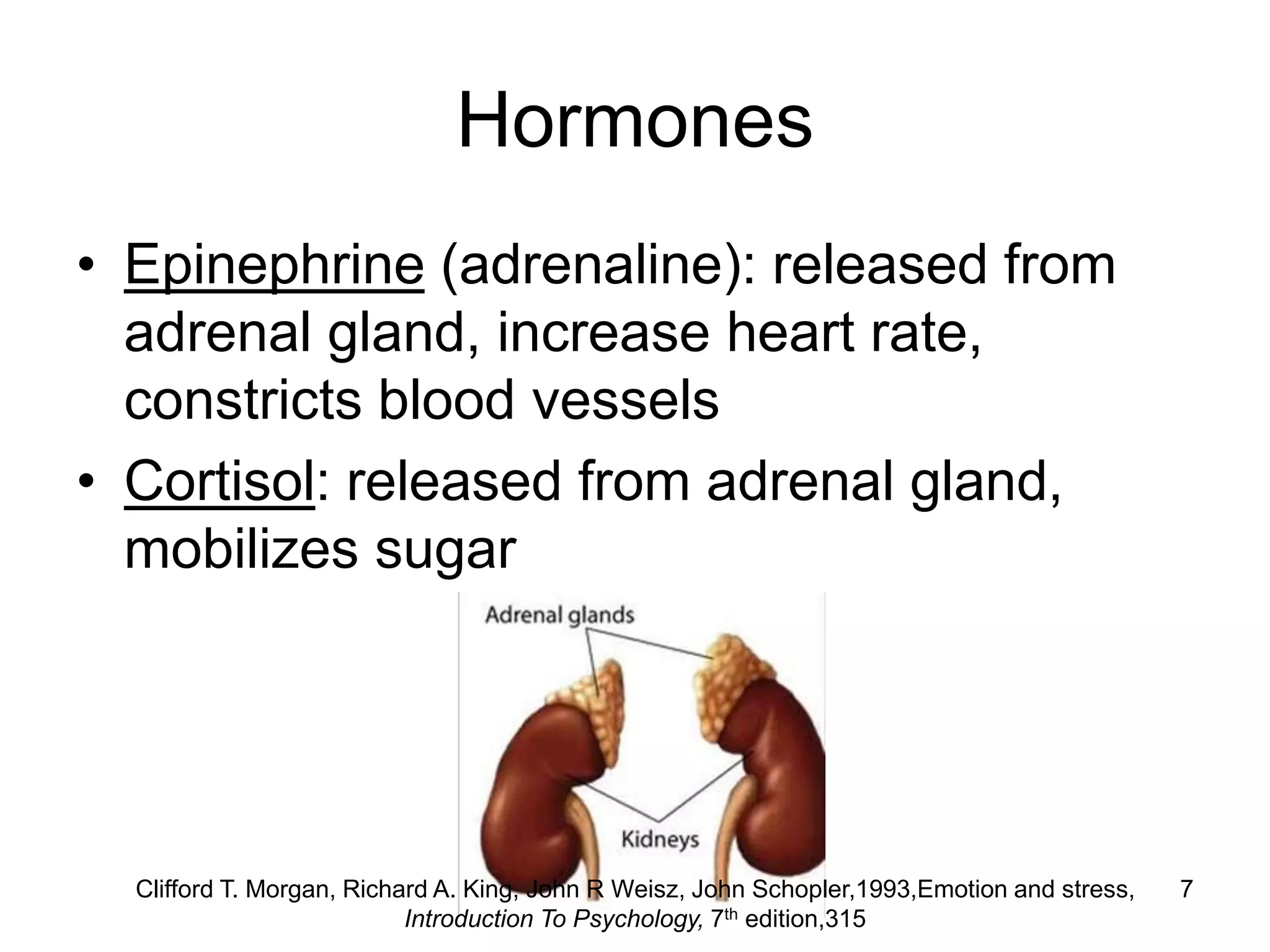
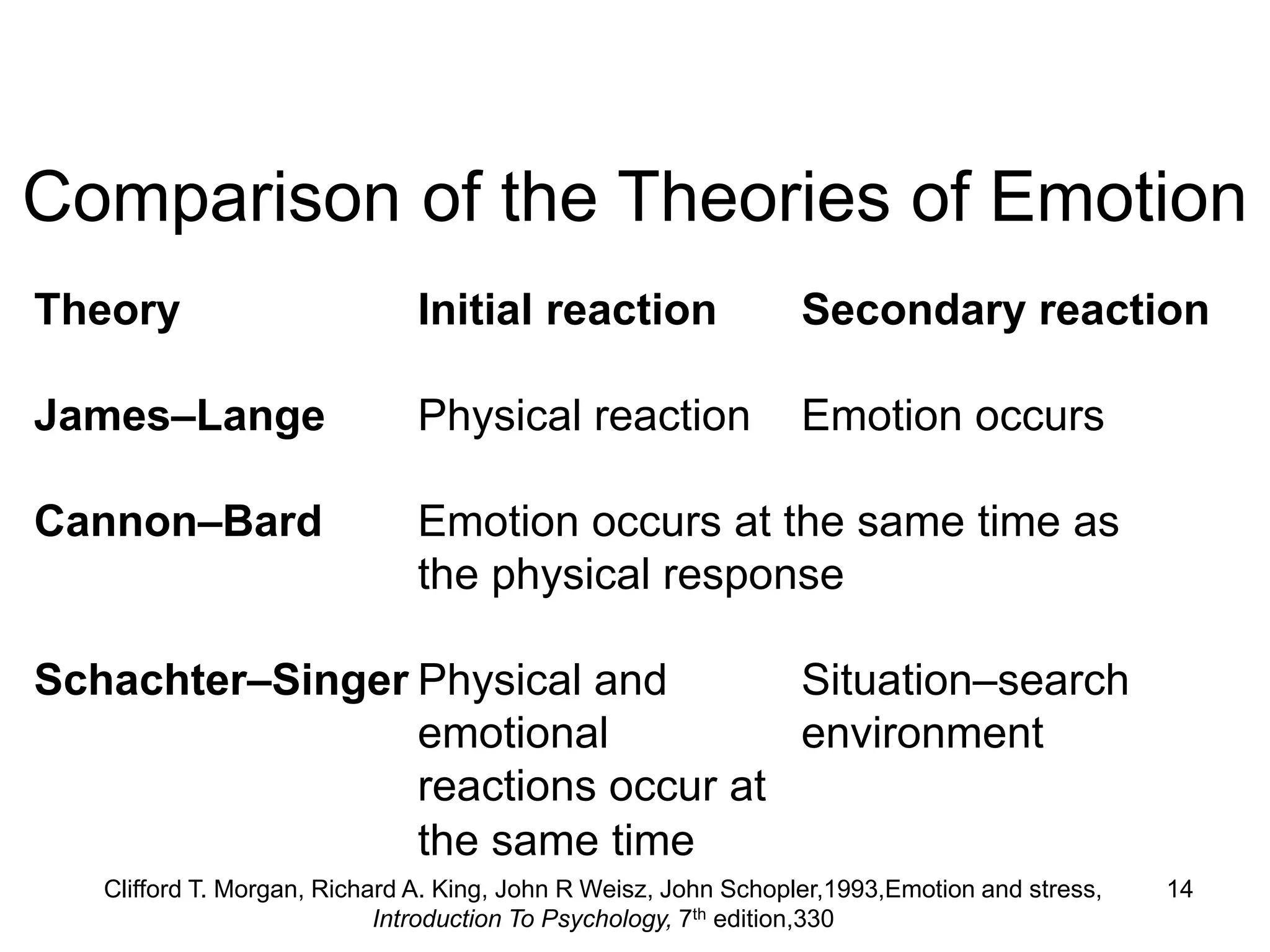
The document discusses emotions from several perspectives. It defines emotions and explores the physiological components of emotions as well as theories about how emotions originate from stimuli. The James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, and Two-Factor theories are described, which propose different relationships between physiological arousal and emotional experience. Disorders of emotion are also reviewed, looking at abnormalities in expression, arousal, and social context evaluation. Primary emotions like joy, fear and anger are identified along with the roles of the amygdala and prefrontal cortex in processing emotion.