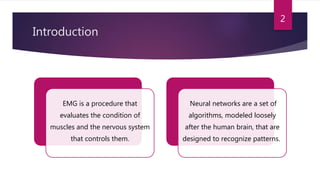
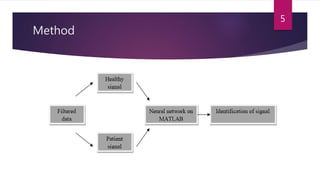
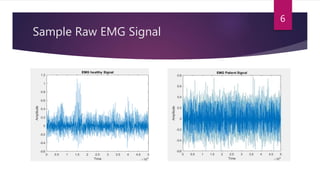
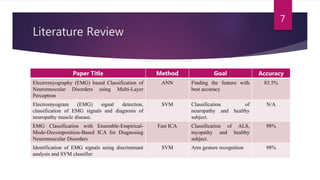
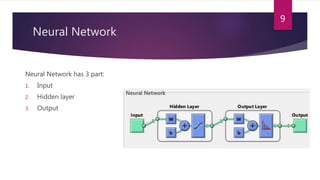
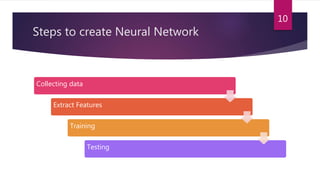
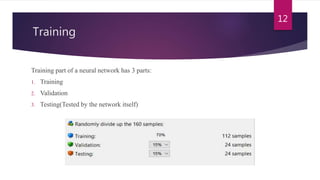
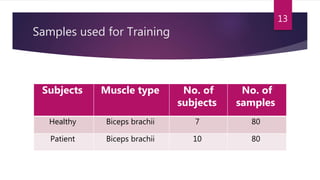
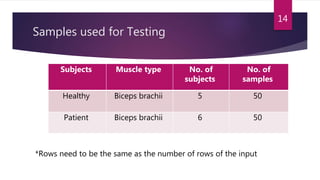
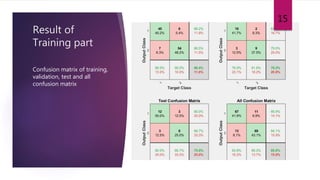
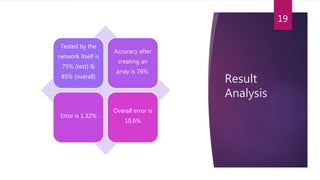
This study aimed to classify EMG signals from healthy and neuromuscular disorder patients using an artificial neural network. Features were extracted from raw EMG signals and used to train and test the neural network. The network achieved 75% accuracy on the test data and 76% accuracy when classifying new samples, with an overall error rate of 10.6%. While the results demonstrated the neural network could classify the EMG signals, the authors concluded the accuracy could be improved and suggested applying convolutional neural networks or improved pre-processing in the future.