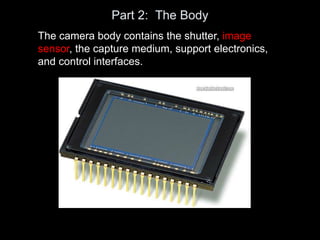
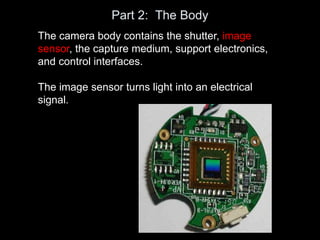
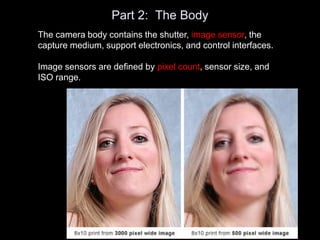
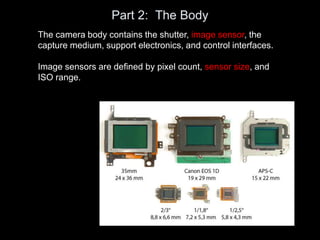
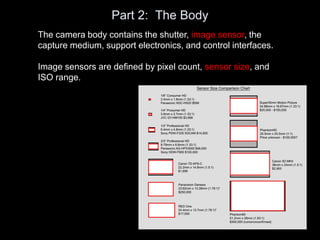
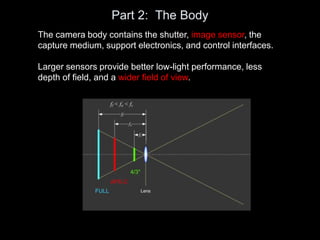
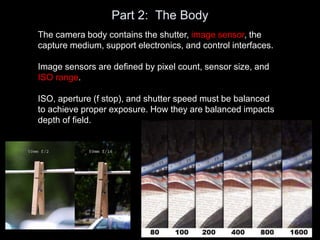
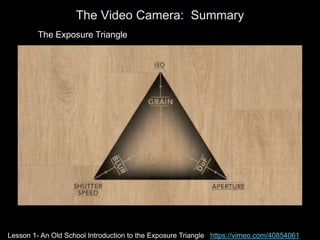
The camera body contains key components like the shutter, image sensor, capture medium, and control interfaces. It also controls important settings such as shutter speed, ISO, white balance, and allows storage of photos/videos via memory cards. Shutter speed, aperture, and ISO must be balanced to achieve proper exposure, and each setting impacts other areas like depth of field and motion blur.