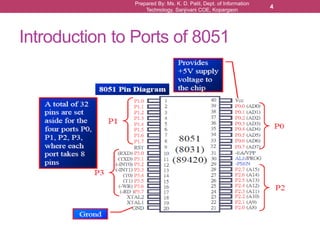
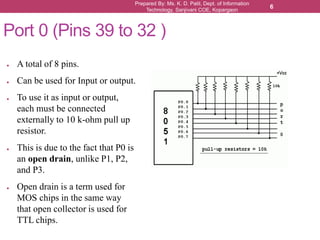
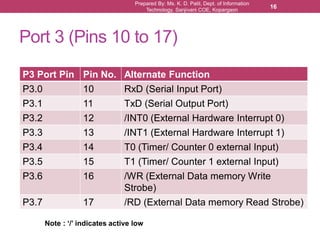
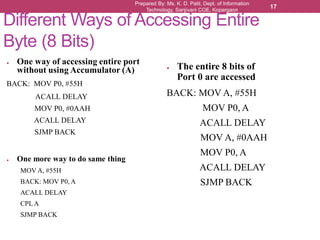
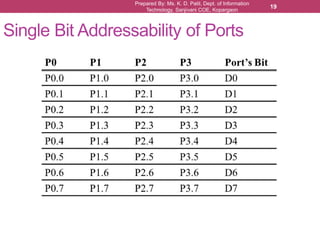
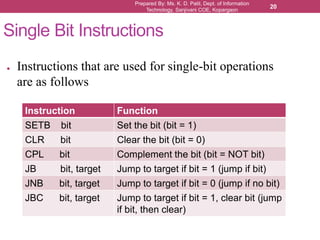
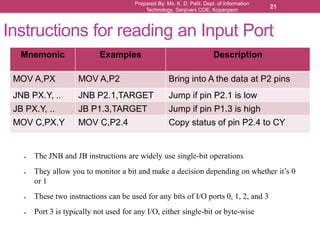
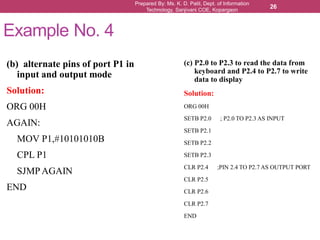
The document outlines the programming and functionalities of I/O ports on the 8051 microcontroller, detailing the characteristics and configurations of ports P0, P1, P2, and P3. It explains individual and byte addressability, as well as provides sample assembly code to demonstrate various I/O operations like sending and receiving data. Additionally, it describes the alternate functions of port 3 and includes examples to illustrate the practical applications of using these ports.