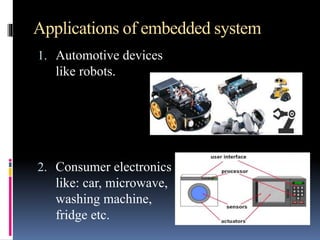
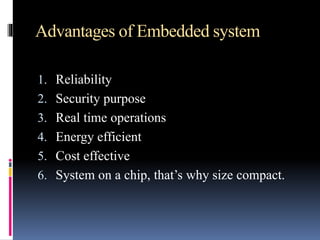
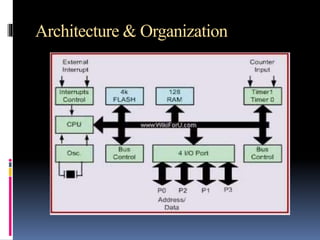
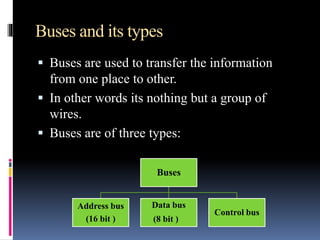
An embedded system is a microprocessor-based combination of hardware and software designed for specific functions, commonly found in automotive devices and consumer electronics. Advantages include reliability, security, real-time operation, energy efficiency, and compact size. Microprocessors and microcontrollers differ in architecture, with microcontrollers integrating memory and I/O ports, while microprocessors require external connections.