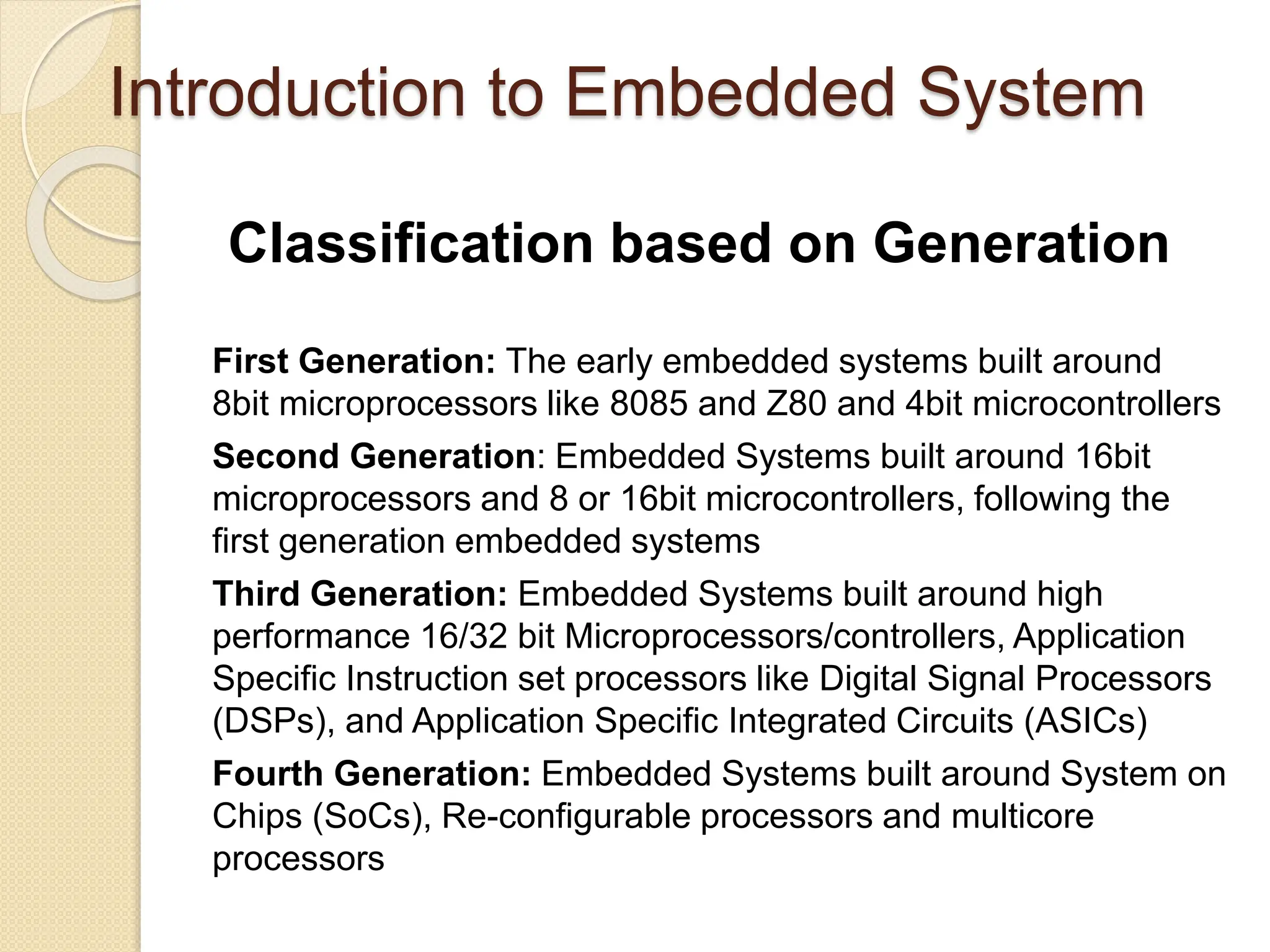
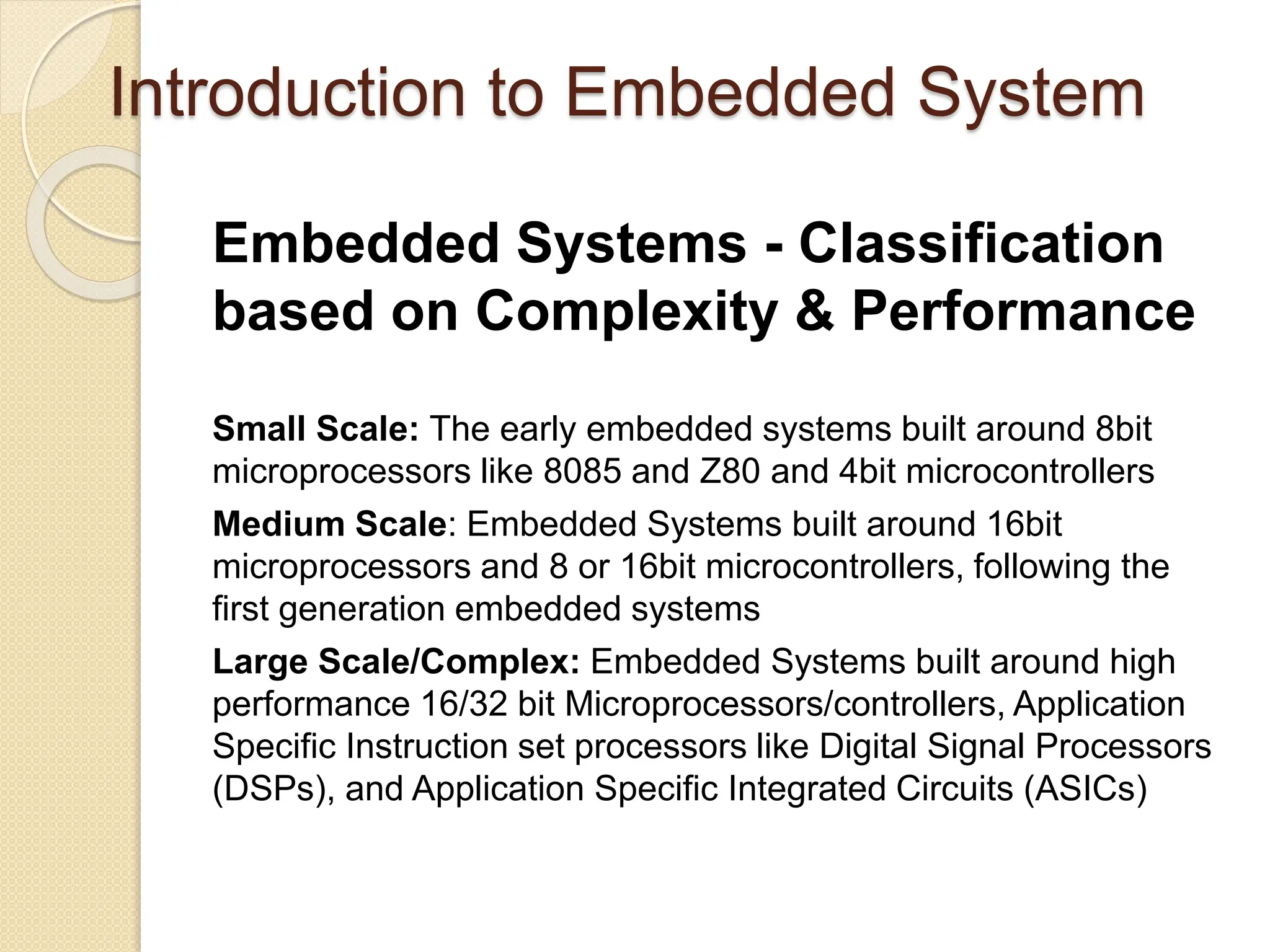
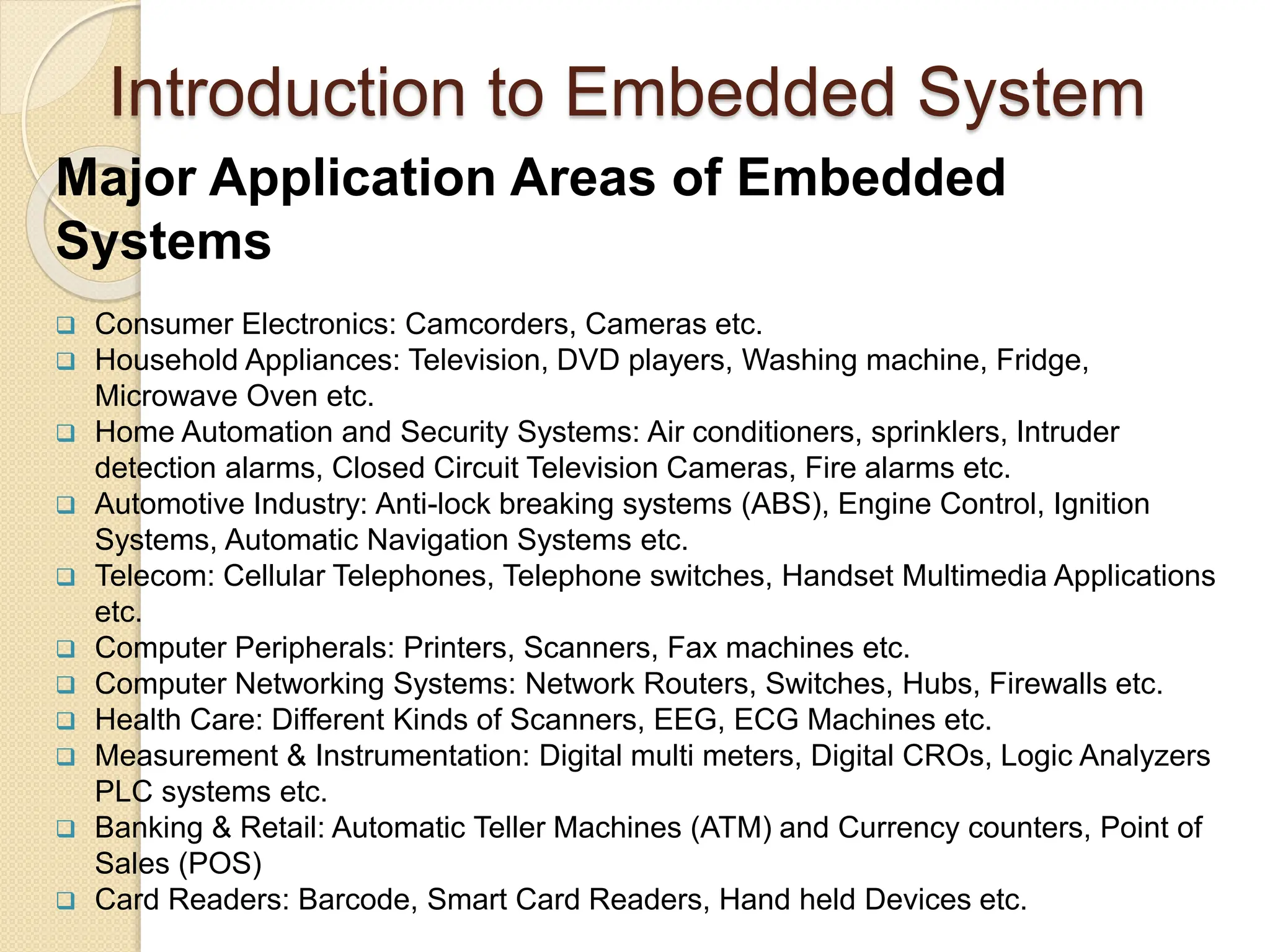
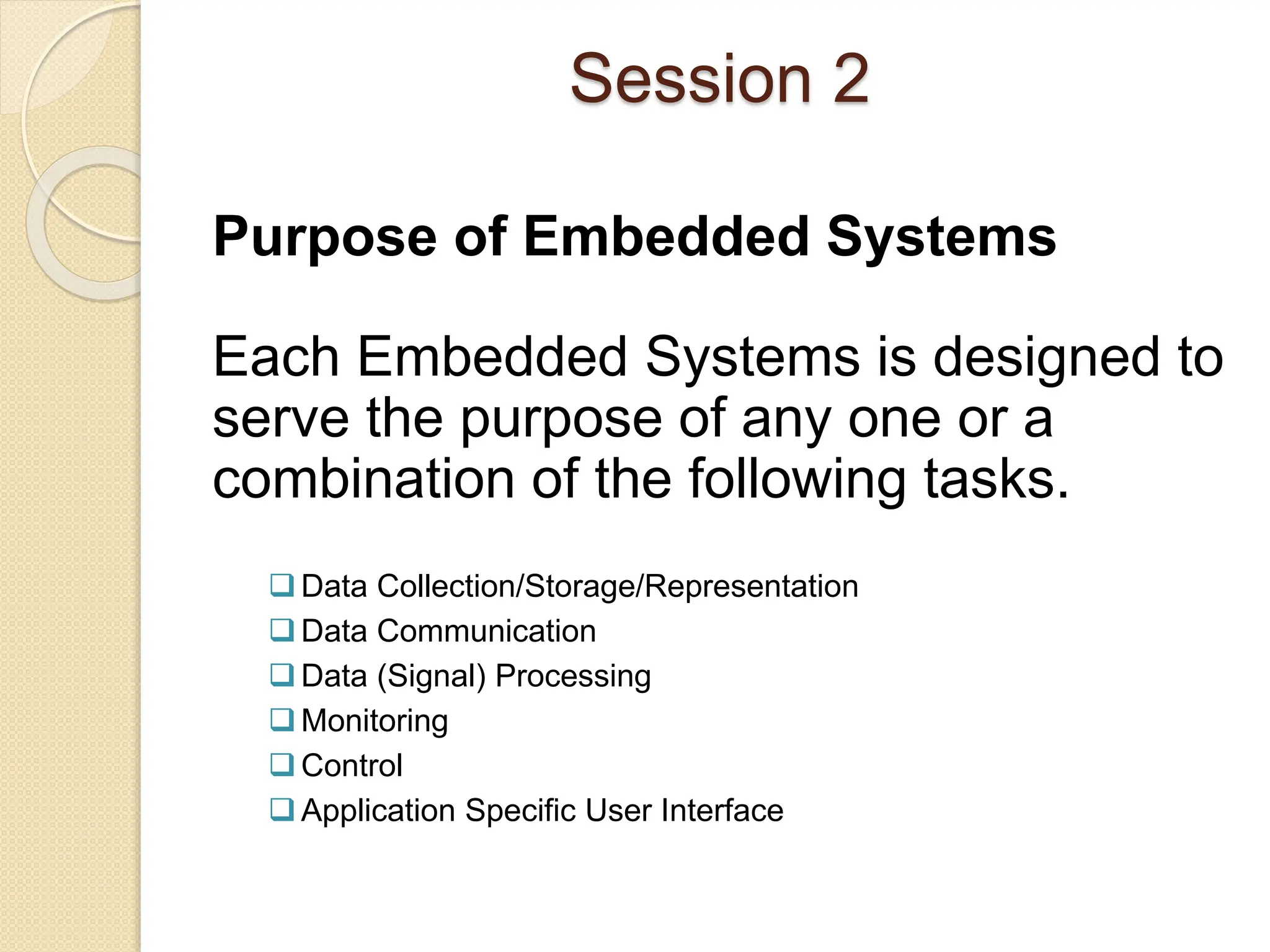
The document provides an overview of embedded systems, defining them as electronic systems designed for specific functions, comprising both hardware and firmware. It classifies embedded systems based on generation, complexity, and performance, with application areas ranging from consumer electronics to healthcare. The session concludes with the exploration of purposes for embedded systems, including data collection, communication, and monitoring.