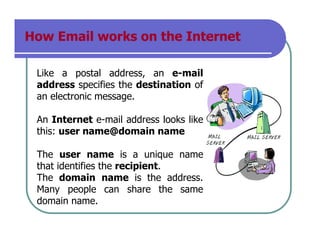
Electronic mail (email) is the most widely used service on the Internet. Email allows users to send messages to one or many recipients anywhere in the world almost instantly. An email address contains a username and domain name separated by an "@" symbol. Emails are sent and received through mail servers and delivered between servers using standard protocols. Attachments can also be included with emails to share files. Basic email functions include composing, sending, receiving, replying, and organizing messages into folders.