This document provides an overview of email, including:
- A brief history, noting that Ray Tomlinson invented internet-based email in 1971 using the @ symbol to indicate a user and host computer.
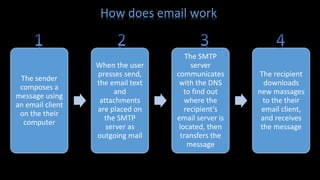
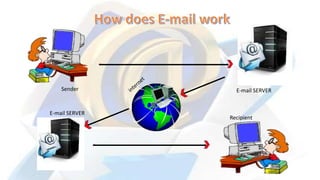
- An explanation of how email works, from a sender composing a message, it being sent to an SMTP server and found the recipient's server, and then the recipient downloading the message.
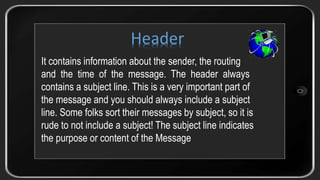
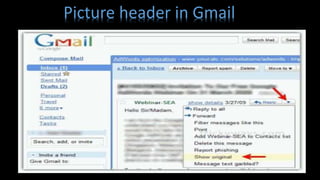
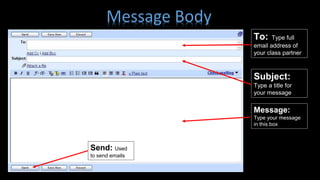
- The key parts of an email, including the header with information like sender, subject, date, and the message body containing the actual content.