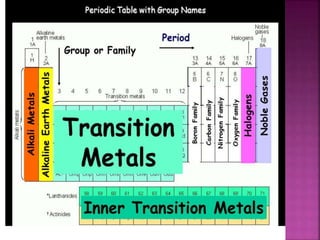
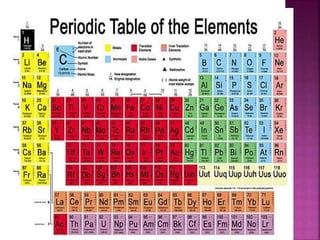
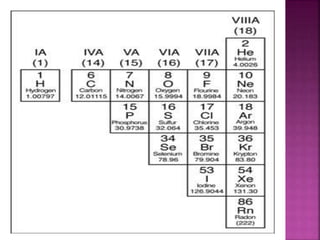
The document summarizes several families in the periodic table and their properties. The IA family contains alkali metals like sodium and potassium that lose one electron in reactions. The IIA family contains alkaline earth metals like calcium that lose two electrons. The VIIA family contains halogens like chlorine and iodine that gain one electron. The VIII family contains noble or inert gases like helium and neon that are very unreactive. Metalloids have properties between metals and nonmetals. Transition metals are elements in the d-block that can form cations with incomplete d subshells.









![ The IUPAC definition[1] defines a transition
metal as "an element whose atom has a
partially filled d sub-shell, or which can give
rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-
shell“
Many scientists describe a "transition metal"
as any element in the d-block of the periodic
table, which includes groups 3 to 12 on the
periodic table.[2][3] In actual practice, the f-
block lanthanide and actinide series are also
considered transition metals and are called
"inner transition metals".](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/judyannsumaoang-elementalfamiliesandgroups-161219052209/85/elemental-families-and-groups-11-320.jpg)
![ Cotton and Wilkinson[4] follow the IUPAC
definition (see above) which includes
scandium and yttrium on the grounds that
they at least have a partially filled d
subshell in the metallic state. However
even this does not (so far) seem to confer
catalytic properties on them which is so
characteristic of the transition metals in
general. Lanthanum and actinium are
included with the lanthanides and
actinides respectively.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/judyannsumaoang-elementalfamiliesandgroups-161219052209/85/elemental-families-and-groups-12-320.jpg)