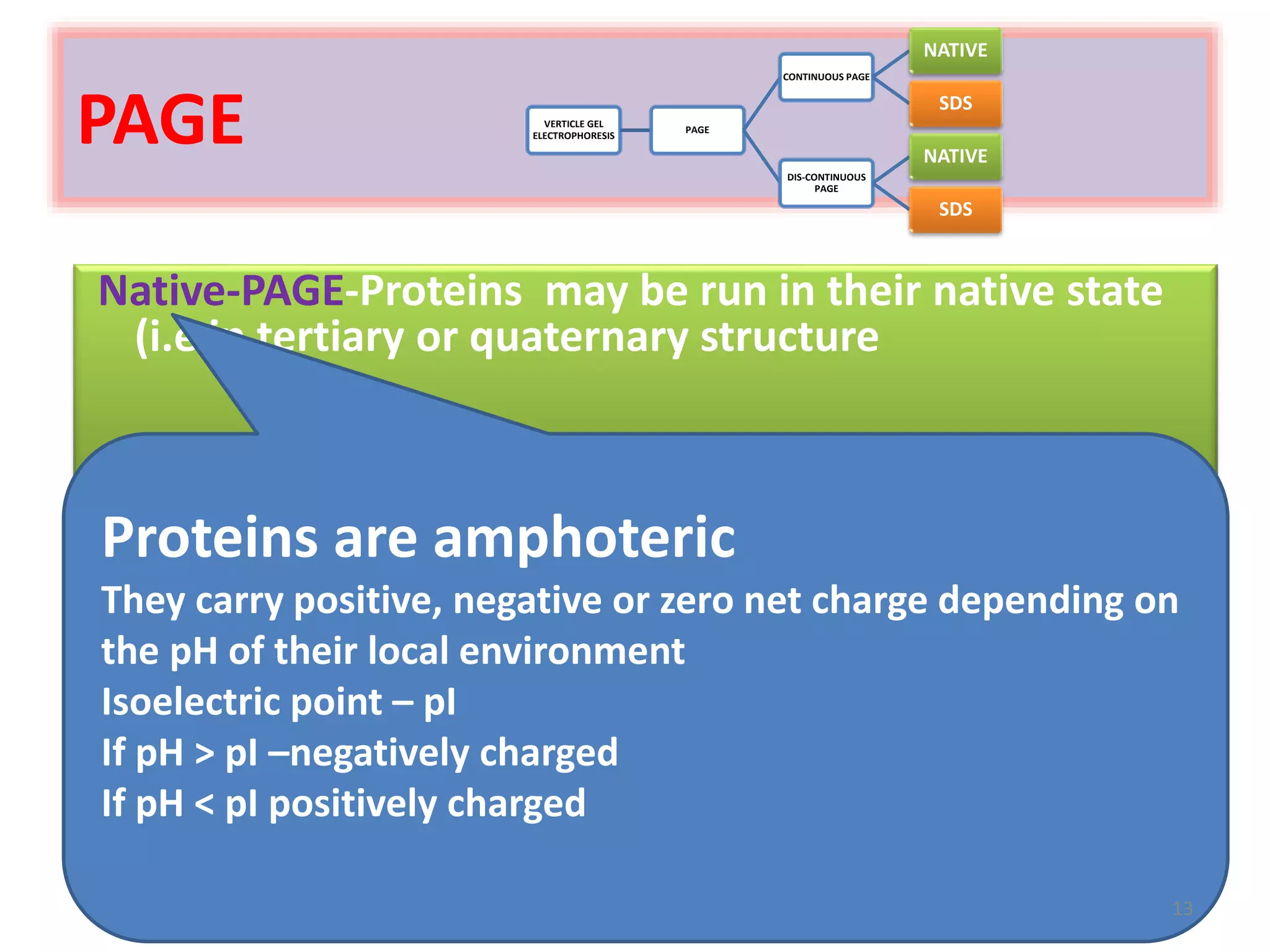
Vertical gel electrophoresis has several advantages over horizontal gel electrophoresis. It allows for the use of a discontinuous buffer system to separate proteins, which is not possible with horizontal gels. The technique involves pouring an acrylamide gel between glass plates to a thickness of less than 2 mm. Samples are loaded and subjected to an electric current, with cations moving toward the cathode and anions toward the anode. Proteins are separated based on their size and charge using techniques like SDS-PAGE, which involves denaturing proteins to impart a uniform charge.