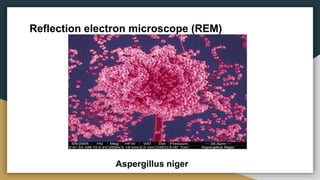
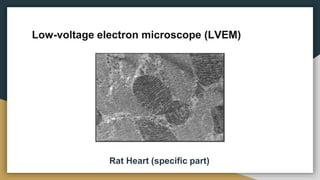
This document discusses electron microscopy and its use to study microorganisms. It describes different types of electron microscopes, including transmission electron microscopes (TEM), scanning electron microscopes (SEM), reflection electron microscopes (REM), scanning transmission electron microscopes (STEM), and low-voltage electron microscopes (LVEM). Each type of microscope is explained in terms of its working principle and resolution. Examples are given of specific microorganisms that have been imaged using different electron microscopes, such as E. coli with TEM, Candida albicans with SEM, Aspergillus niger with REM, and plant and rat heart cells with other types. In summary, electron microscopes provide higher magnification than light