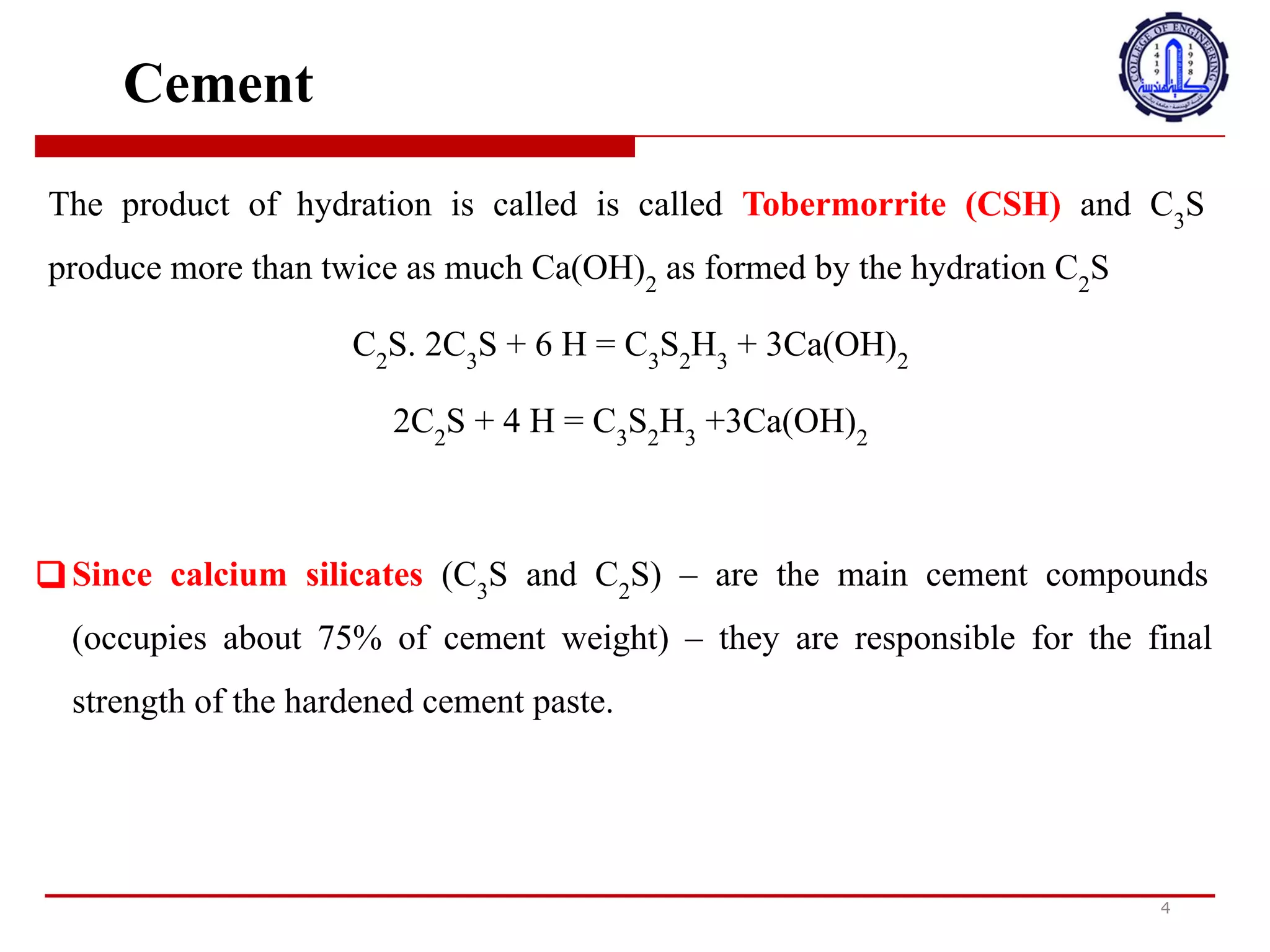
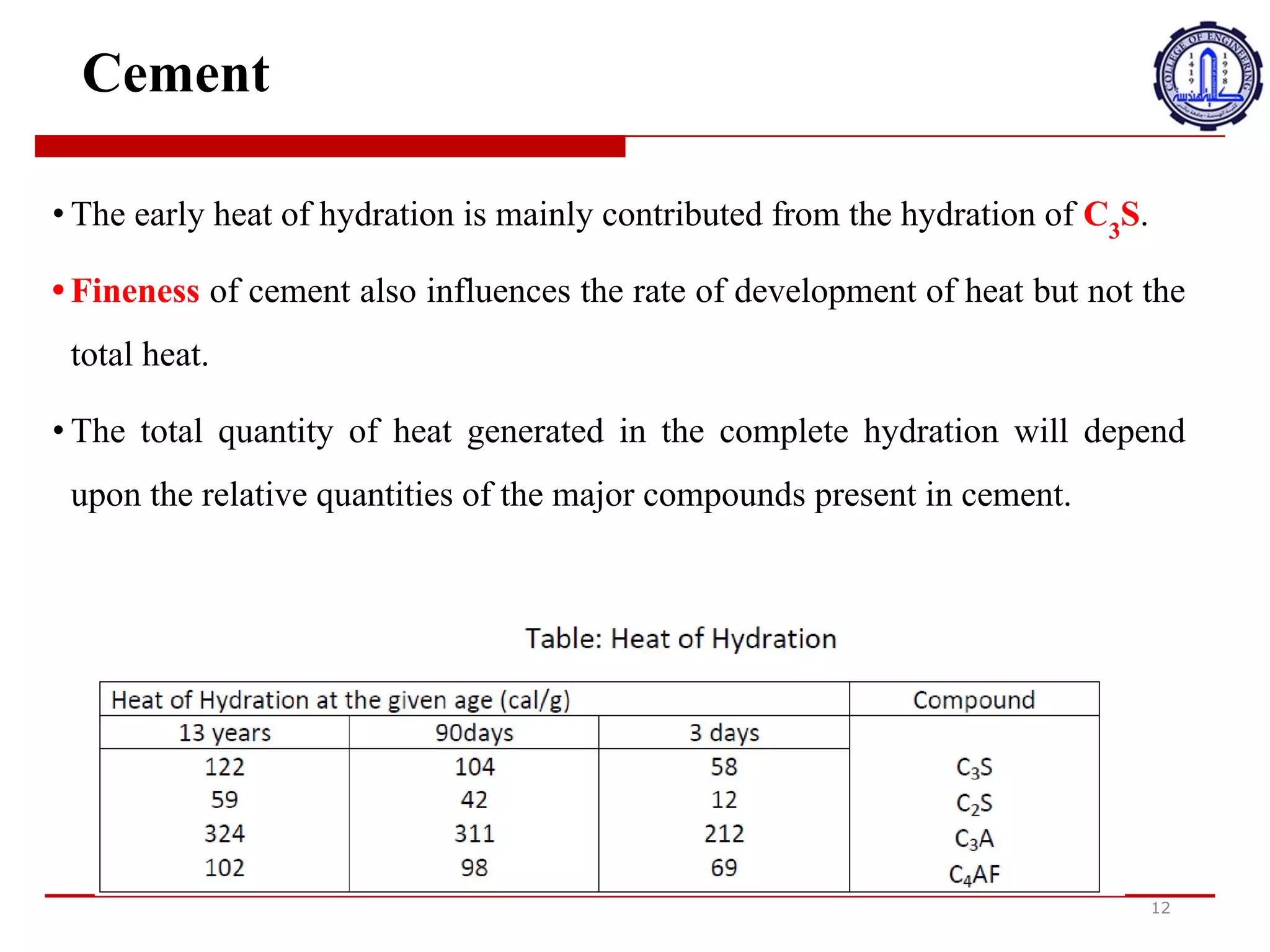
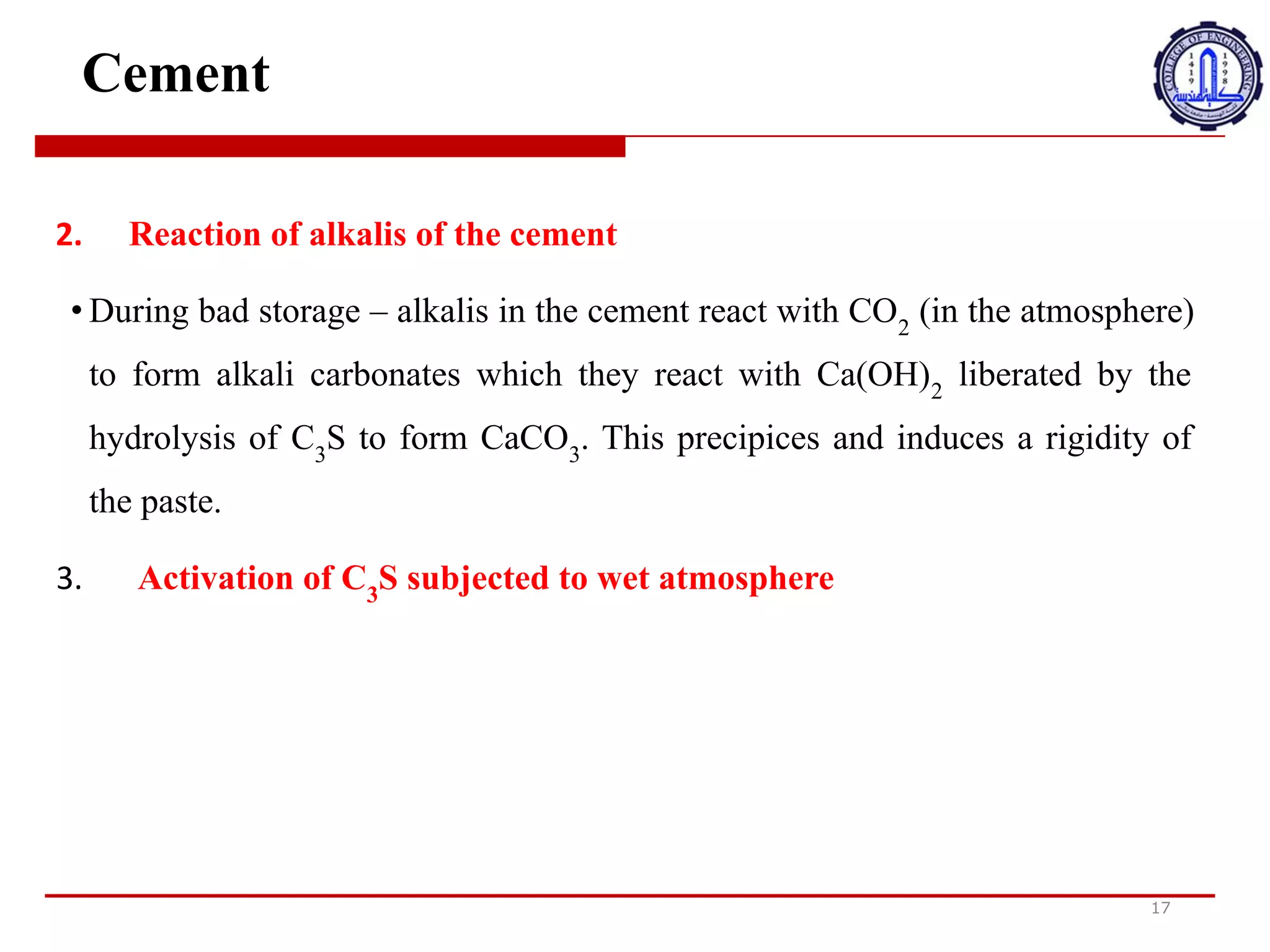
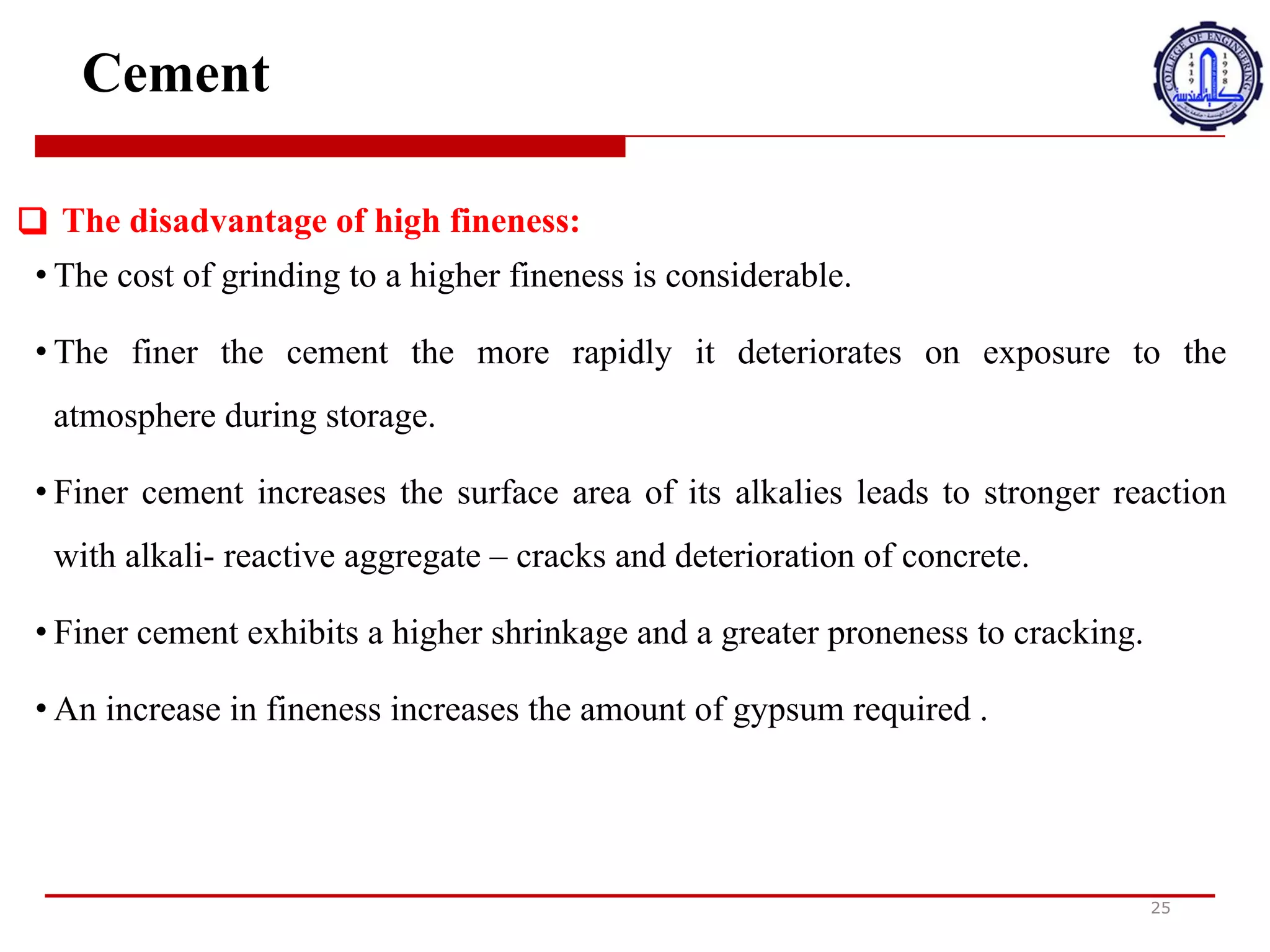
The document discusses cement compounds and hydration. It states that the rates of hydration of C3S and C2S differ in pure form but are affected by interactions when present together in cement. In commercial cement, C3S and C2S contain small impurities that impact hydration properties. Calcium silicates (C3S and C2S) make up around 75% of cement and are responsible for final strength. Tricalcium aluminate (C3A) reacts violently with water but gypsum is added to cement to prevent this and allow proper setting.