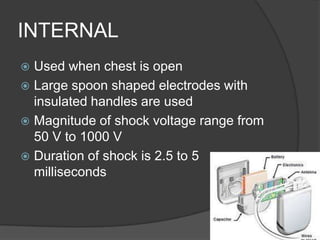
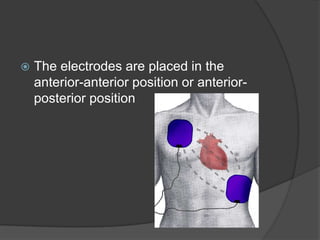
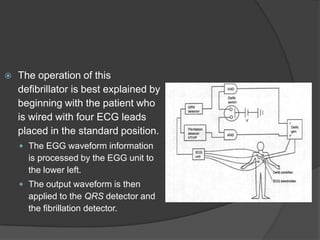
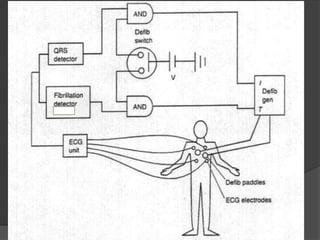
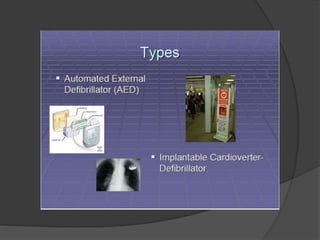
A defibrillator is a device that delivers an electric shock to the heart to stop ventricular fibrillation or atrial fibrillation, which are abnormal heart rhythms. Ventricular fibrillation occurs when the heart's lower chambers quiver instead of pumping blood, which can be fatal if not treated within minutes by delivering a shock via a defibrillator to reset the heart's rhythm. Defibrillators can be external or internal, and use electric shocks of varying voltages and durations depending on the type and location of use to convert the heart rhythm back to normal.