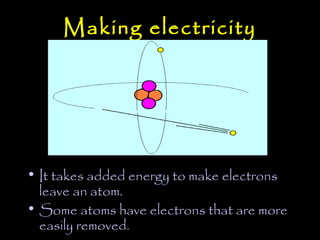
Electricity is produced through the movement of electrons between atoms. Normally, electrons orbit the nucleus of an atom but can be removed by adding energy. Some atoms have outer electrons that are farther from the nucleus and more easily removed. Copper and silver are good electrical conductors because their outer electrons are farther from the nucleus and repelled by multiple electron layers, making them easier to remove with just a small amount of energy. While silver is a slightly better conductor, copper is more commonly used due to its lower cost and greater abundance.