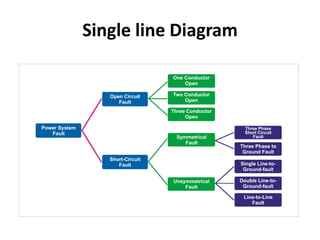
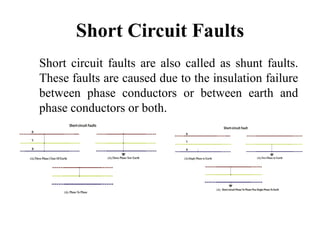
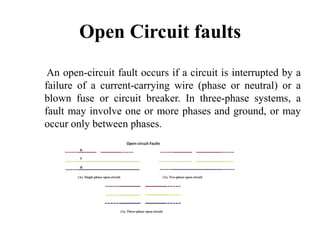
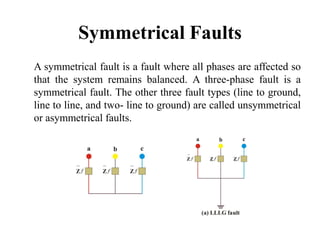
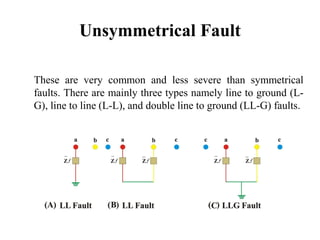
The document discusses various types of underground transmission line faults including short circuits caused by insulation failures, open circuits from broken wires or blown fuses, symmetrical faults affecting all phases equally, and unsymmetrical faults including line to ground, line to line, and double line to ground faults. It also mentions over voltage from poor power regulation, under voltage from increased loads or transformer issues, and over current faults from short circuits. Insulation heating problems from air infiltration or moisture are discussed. The document provides a circuit diagram for testing faults and lists components used. Causes of faults include broken conductors and safety issues are among the effects.