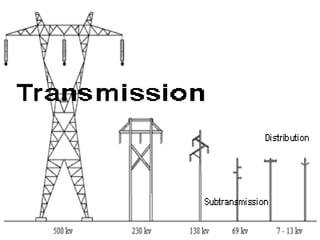
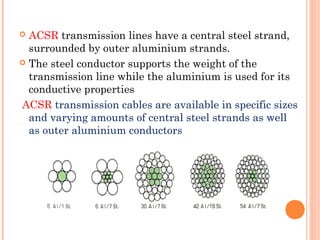
This document discusses transmission lines and overhead power lines. It describes different types of transmission lines like coaxial cable, microstrip, and twisted pair. It then covers overhead power lines, explaining that they transmit electricity over long distances using conductors like copper, steel, aluminum, and ACSR. The document also classifies overhead transmission lines by voltage and discusses conductor materials and their properties.