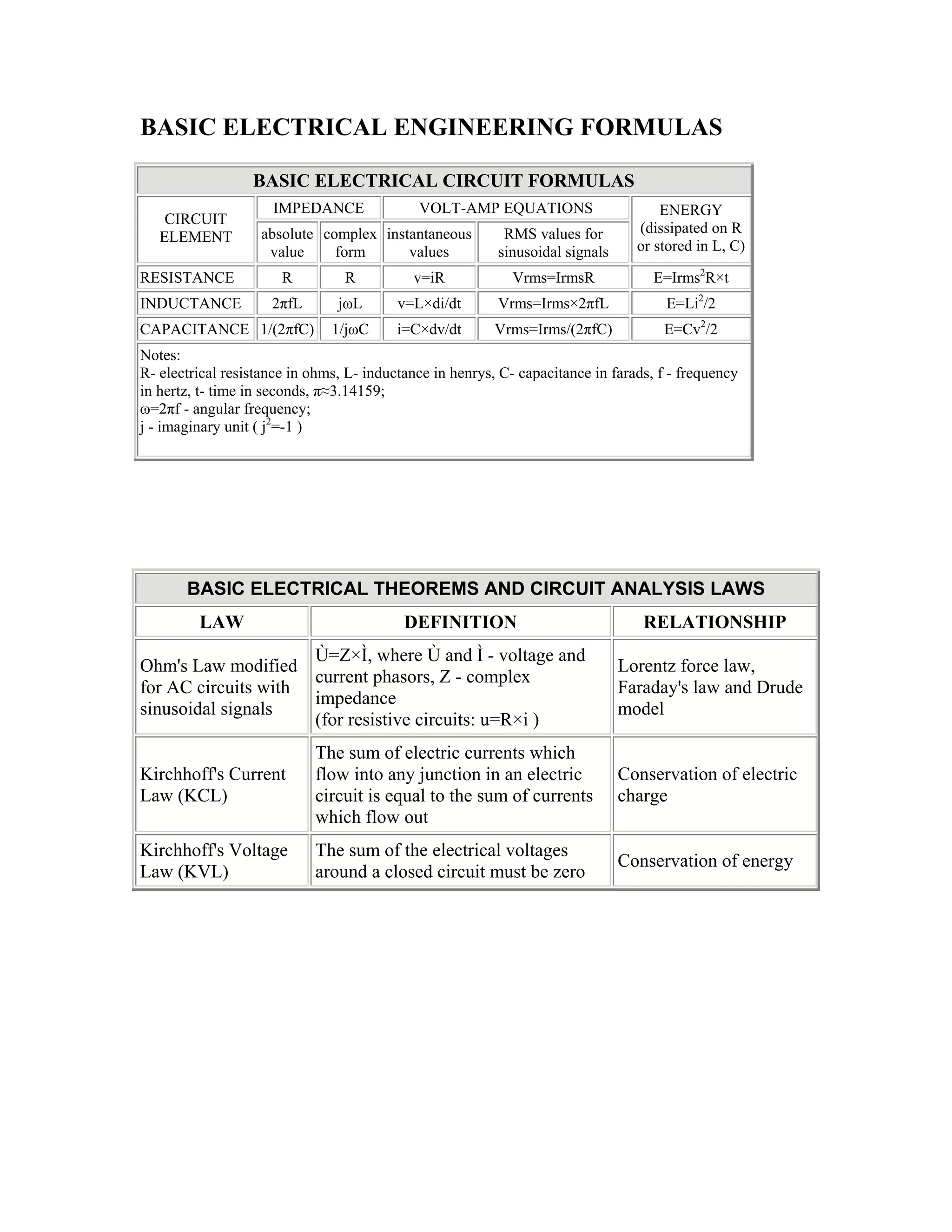
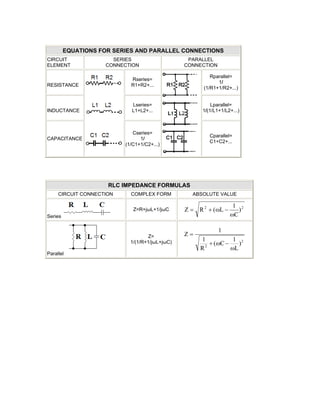
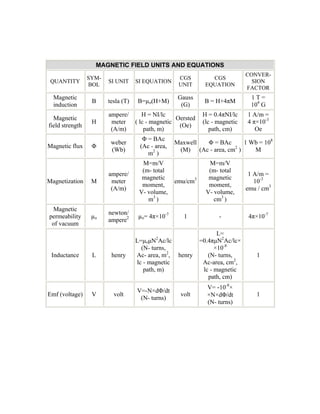
The document provides formulas and equations for basic electrical engineering concepts including circuit elements, Kirchhoff's laws, series and parallel connections, impedance, magnetic fields, Maxwell's equations, and more. It defines relationships for resistance, inductance, capacitance, voltage, current, impedance, magnetic induction, flux, and other quantities. Formulas are given for both SI and CGS units with conversion factors. Series and parallel combinations of resistance, inductance and capacitance are also summarized.