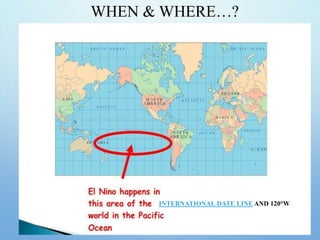
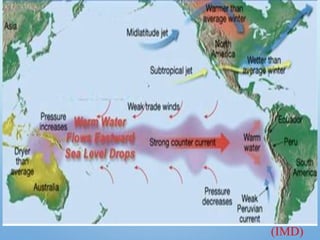
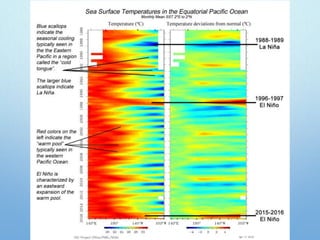
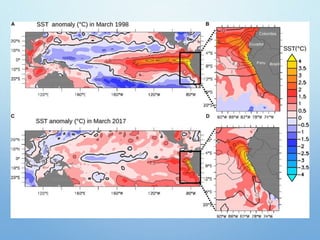
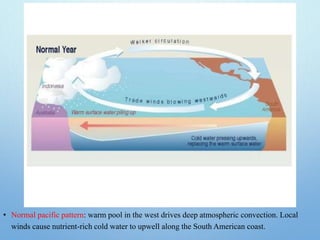
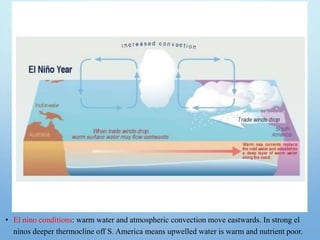
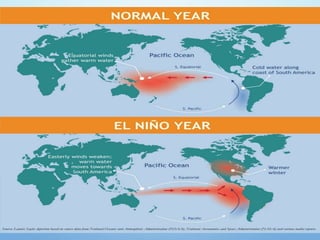
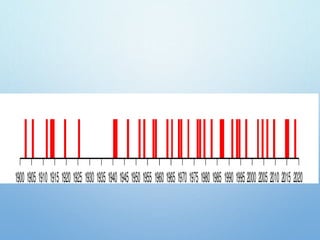
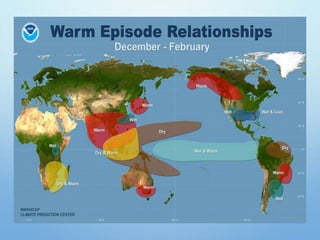
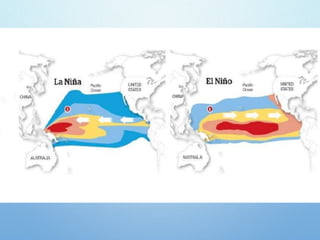
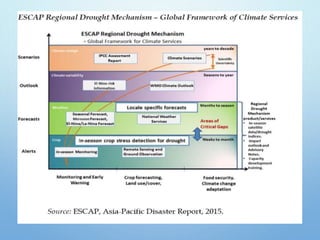
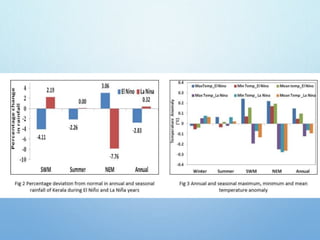
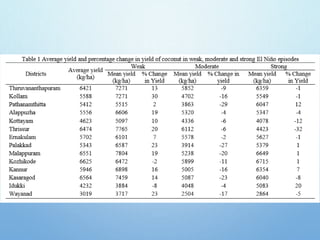
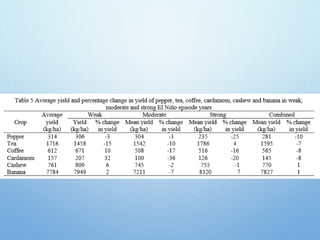
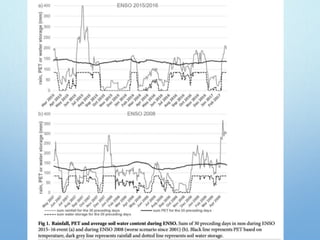
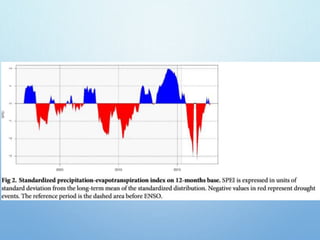
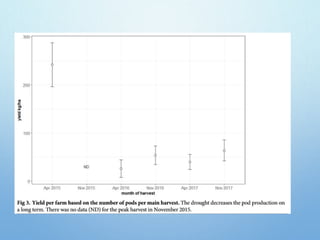
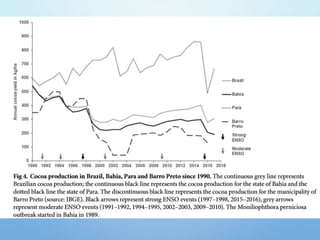
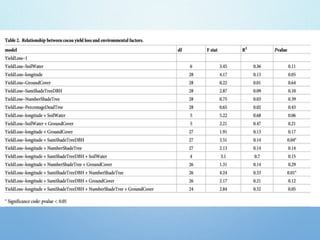
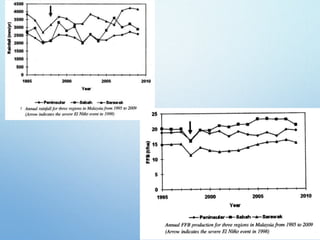
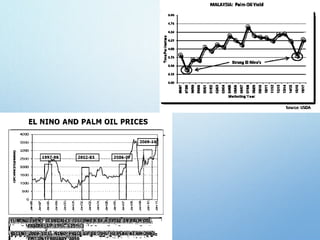
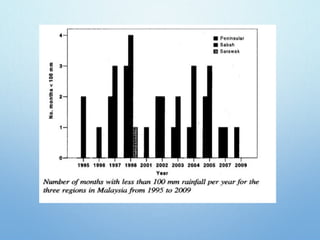
El Niño is a climate pattern characterized by warmer-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the tropical Pacific Ocean, occurring every 3 to 7 years and lasting about a year. It impacts weather patterns globally, causing phenomena such as drought in Australia and heavy rainfall in South America, while affecting fisheries and agriculture. Scientists predict El Niño events by monitoring temperature changes in the ocean, with significant effects observed, including billions in weather-related damages and food insecurity in various regions.