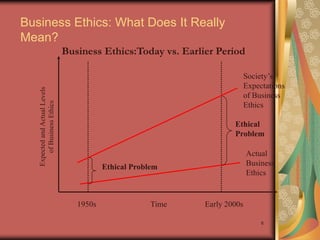
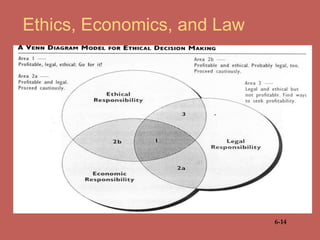
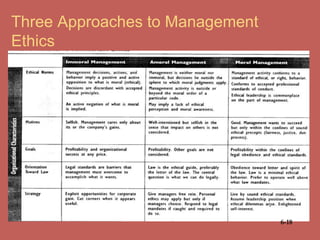
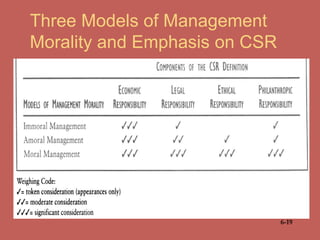
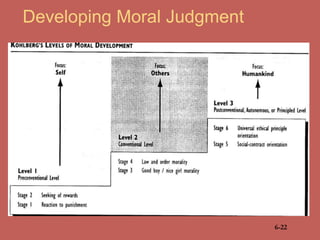
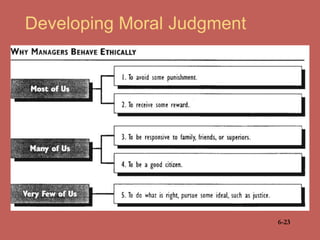
This document discusses business ethics fundamentals and provides an overview of key concepts. It defines business ethics as practices and behaviors that are good or bad within a moral duty context. Three models of management ethics are discussed: immoral management which lacks ethical principles, moral management which conforms to high ethical standards, and amoral management which does not adequately consider ethics. Developing moral judgment requires considering external influences on values as well as cultivating internal qualities like moral imagination and a sense of obligation.