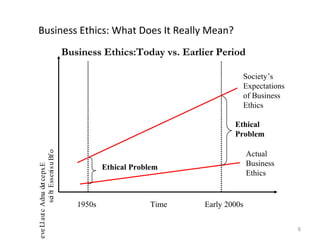
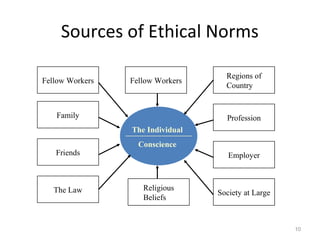
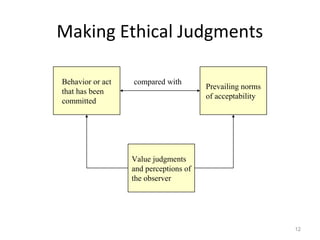
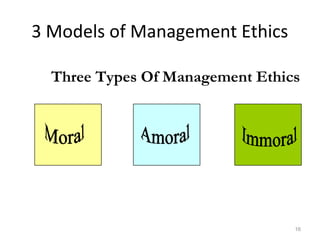
The document discusses key concepts in business ethics including:
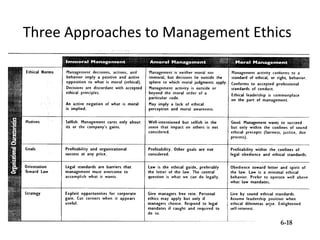
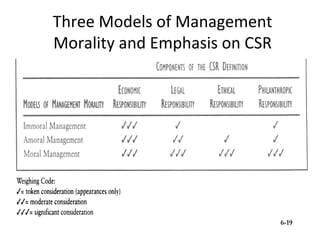
1) Three models of management ethics - immoral, moral, and amoral management.
2) Factors that can make moral management actionable such as support from senior management and ethics training.
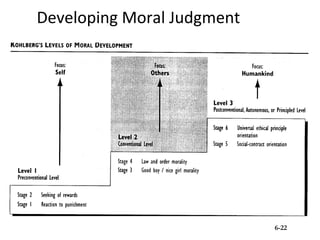
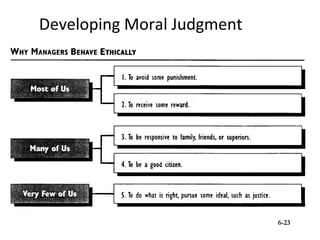
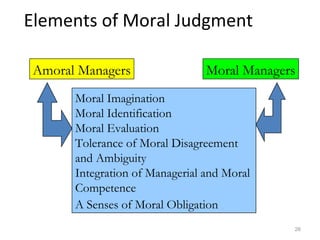
3) Elements of developing moral judgment for managers, including moral imagination, identification, evaluation, and a sense of moral obligation.