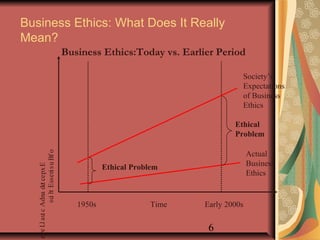
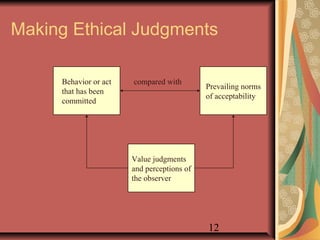
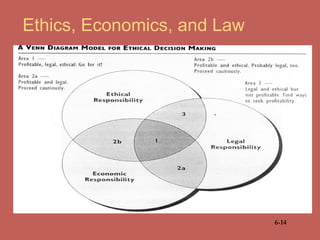
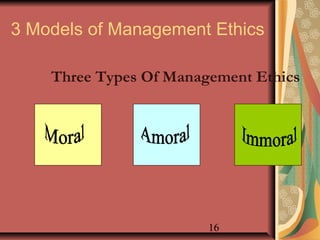
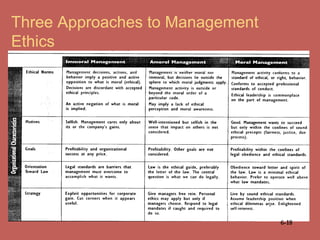
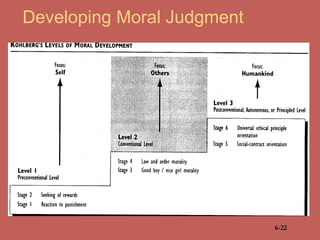
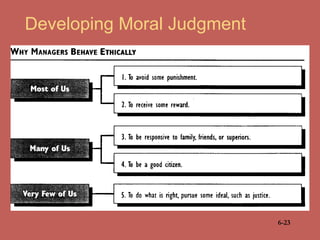
This document provides an overview of business ethics fundamentals. It discusses the increased public interest in business ethics in recent decades and outlines key ethical issues like employee relations. The document defines business ethics and describes two branches of ethics. It also presents three models of management ethics: immoral, moral, and amoral management. The document concludes by discussing elements of moral judgment and key terms in business ethics.