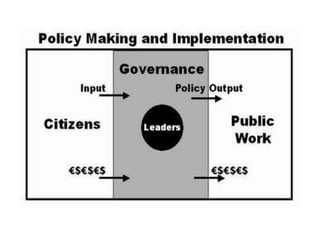
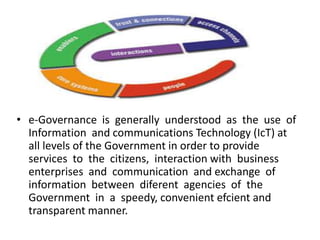
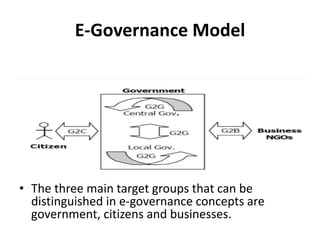
E-governance, introduced in the early 1990s, utilizes information and communication technology to enhance government services and promote transparency in India. It encompasses various interactions including government-to-citizen and government-to-business, with objectives to improve service delivery and citizen engagement. While e-governance projects like Bhoomi in Karnataka and Gyandoot in Madhya Pradesh have showcased successful implementations, challenges such as technological accessibility, infrastructure, and local customization persist.




































![Dr. Kamal Gulati
Associate Professor |
University Quality Support Head |
Mentoring Programme Coordinator
[Ph. D., M.Sc. (Computer Science), M.C.A., M.B.A]
Professional Certifications:
• Certified Microsoft Innovative Educator
• Data Science 101 Certification from Big Data University
• R Language 101 Certification from Big Data University
• SQL Certification from SOLOLEARN.com
• Certified IBM Big Data 101 from Big Data University
• R Program & Python Certified from DataCamp
• Wiley Certified Big Data Analyst [WCBDA]
• Certification on DBMS from IIT Mumbai
• Certified Cisco Certified Network Associate [CCNA]
• Certified Microsoft Certified Professional [MCP]
• Certified Brainbench in Computer Fundamentals, Microsoft Access, MySQL 5.7 Administration &
Microsoft Project](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/egovernance-171208050505/85/E-Governance-in-Laymen-Terms-44-320.jpg)




