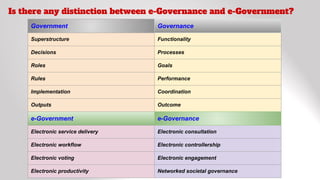
E-governance involves applying information technology to improve government processes and services. It aims to make governance more transparent, accountable, responsive and inclusive. Some key benefits are more efficient resource utilization, reduced delays and corruption, and improved information delivery to citizens. Top implementing countries include Sweden, Denmark, Norway, the US and Netherlands. E-governance initiatives provide various digital services from government to citizens, businesses and other government agencies. However, challenges remain around internet access, literacy, and strengthening legal frameworks around cybersecurity and data protection.