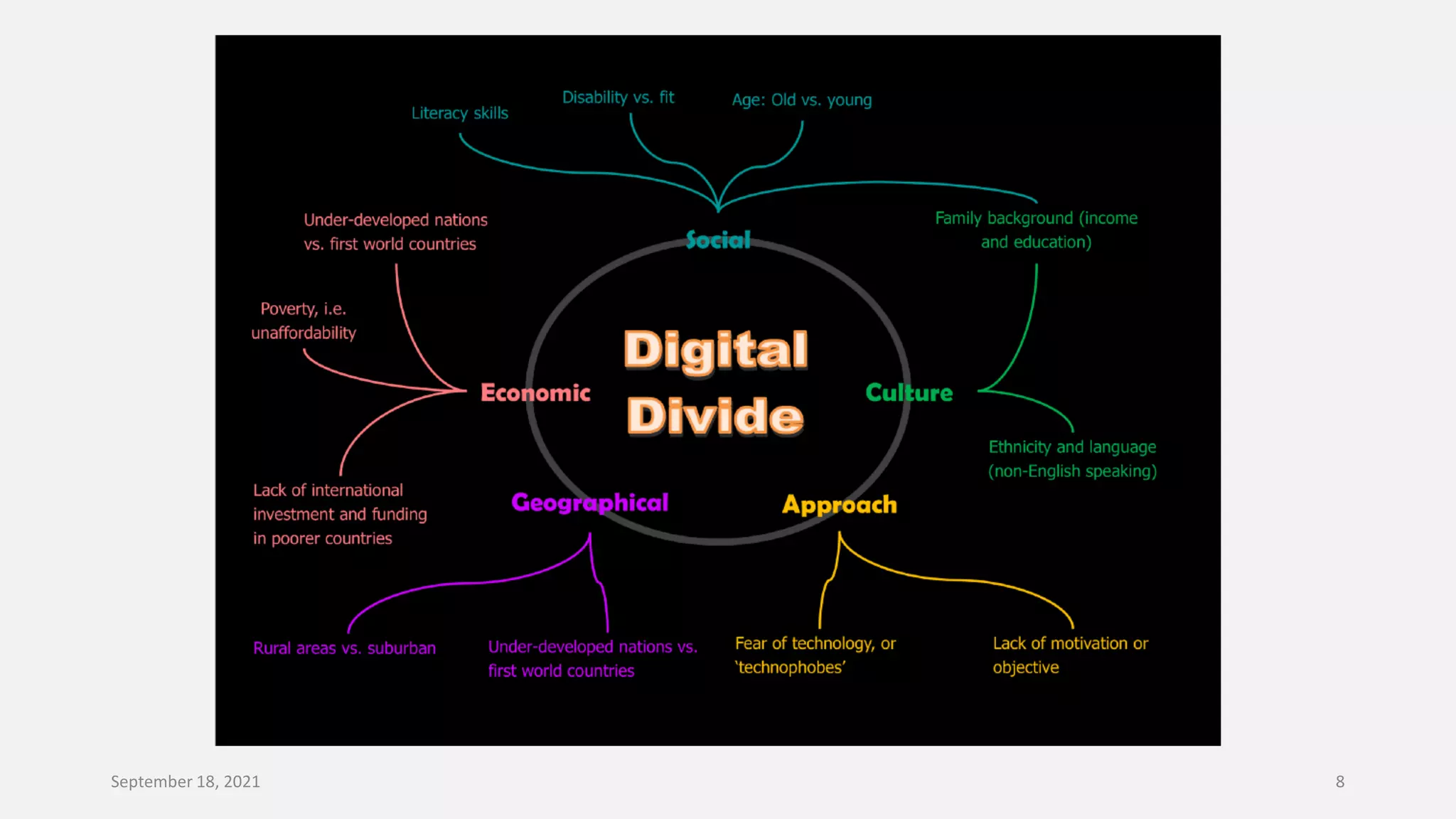
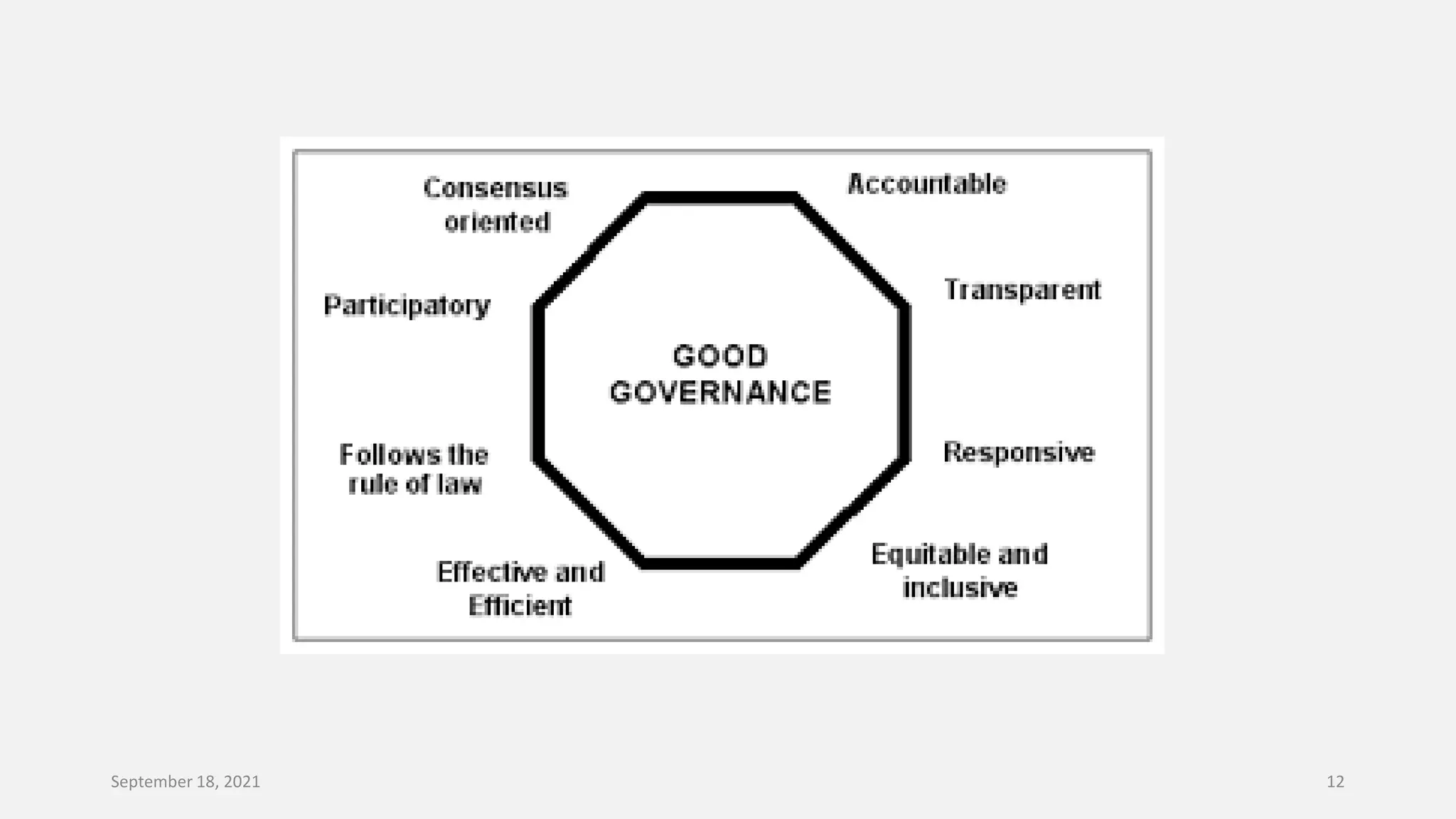
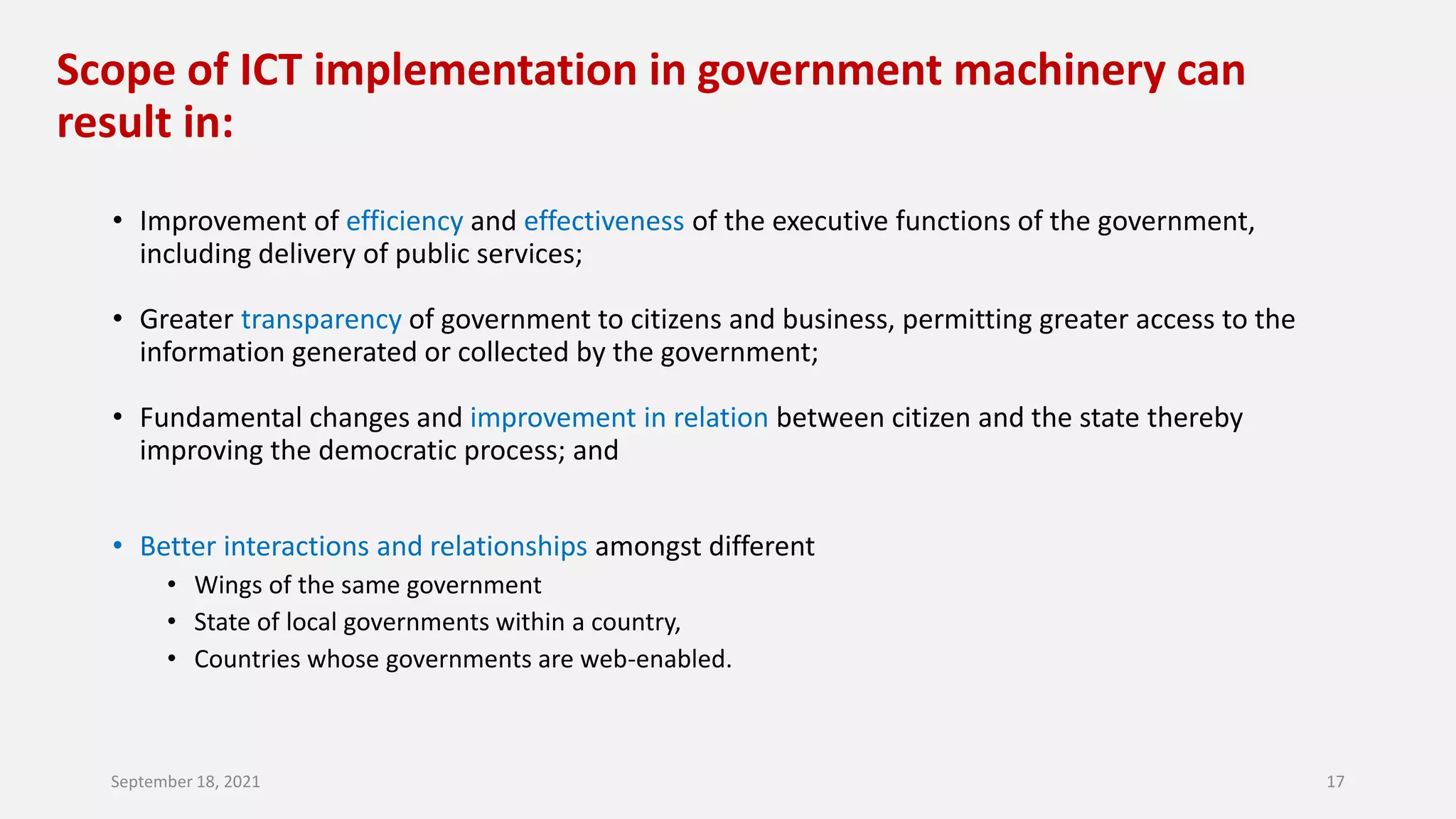
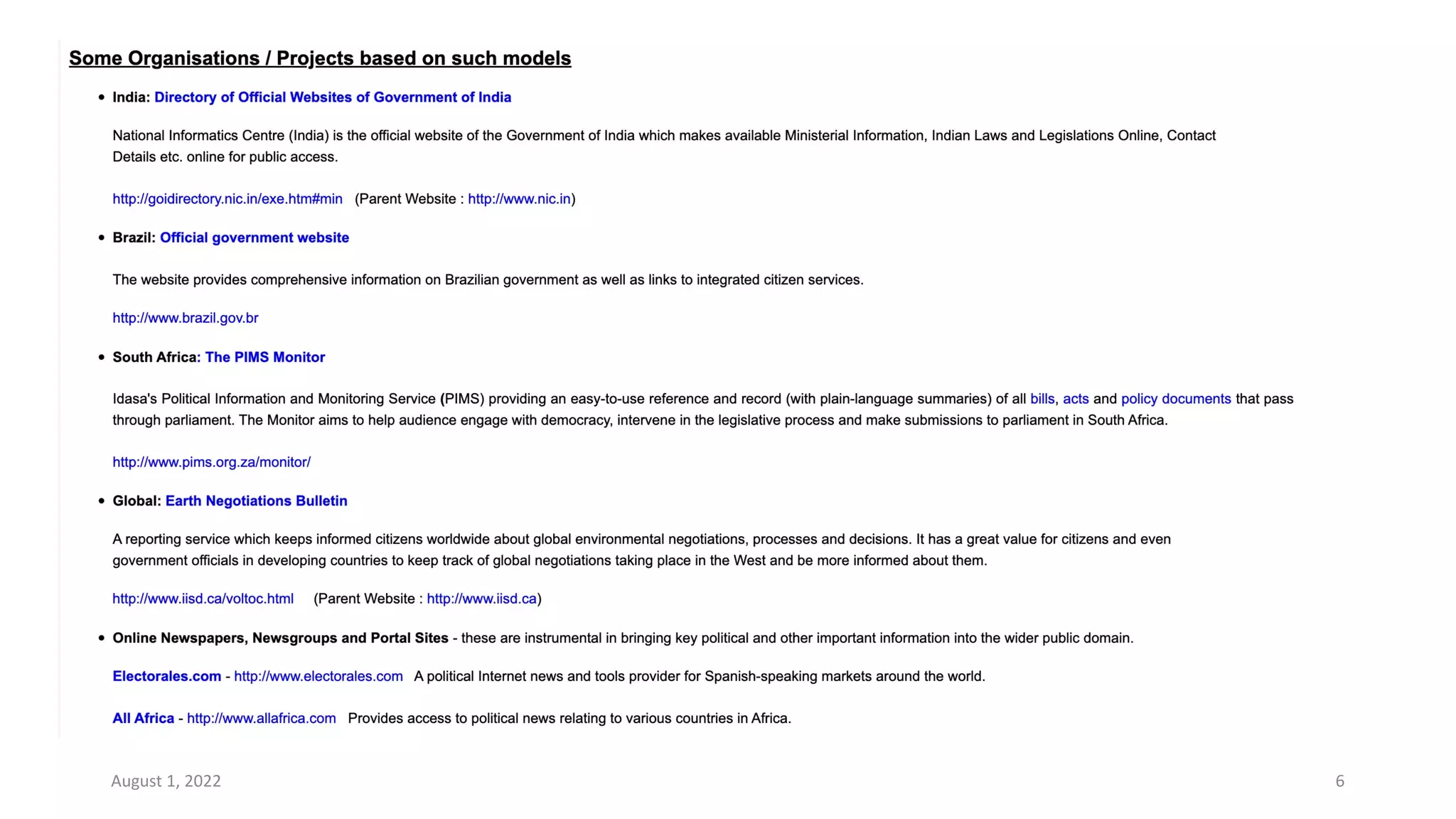
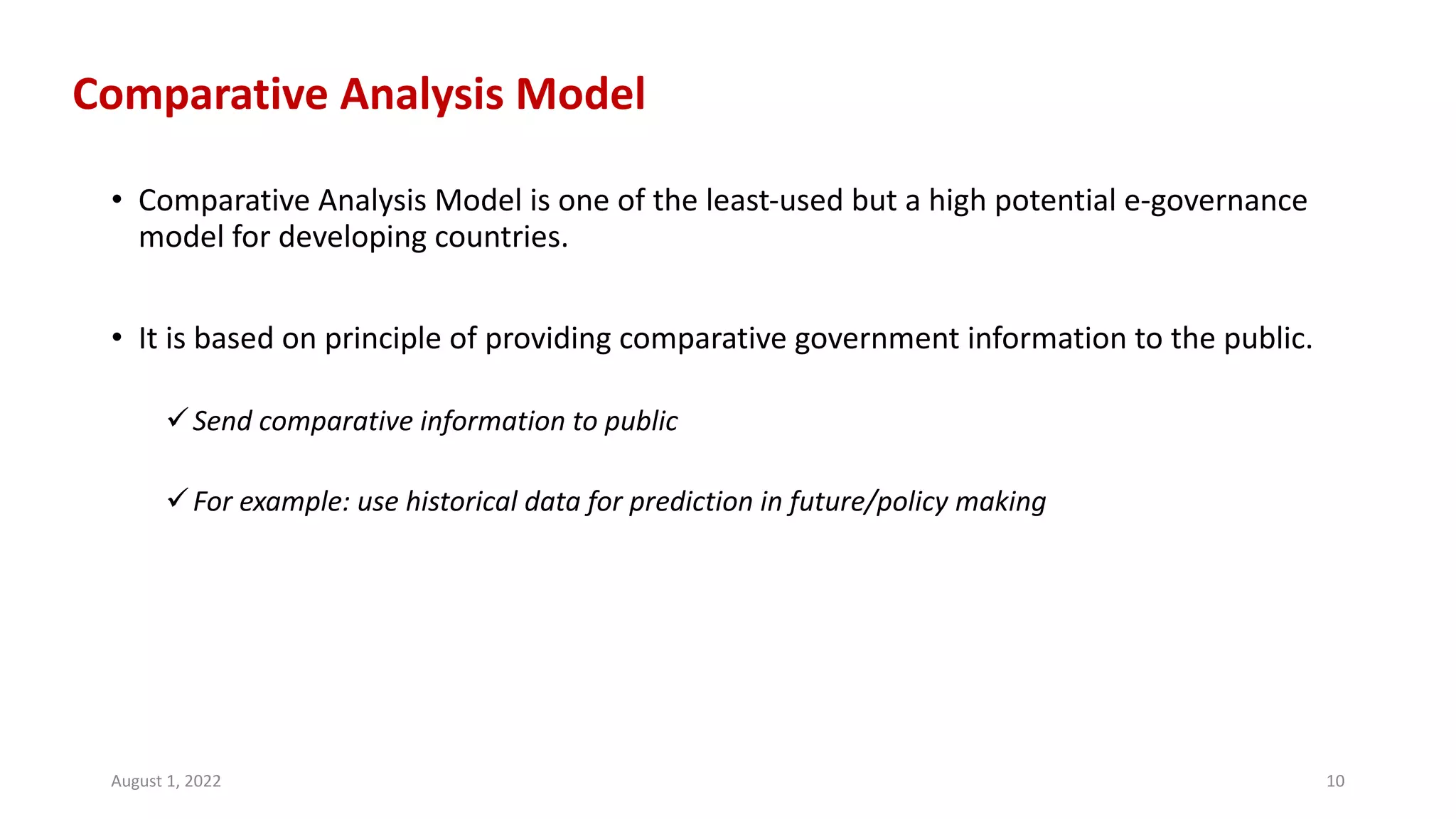
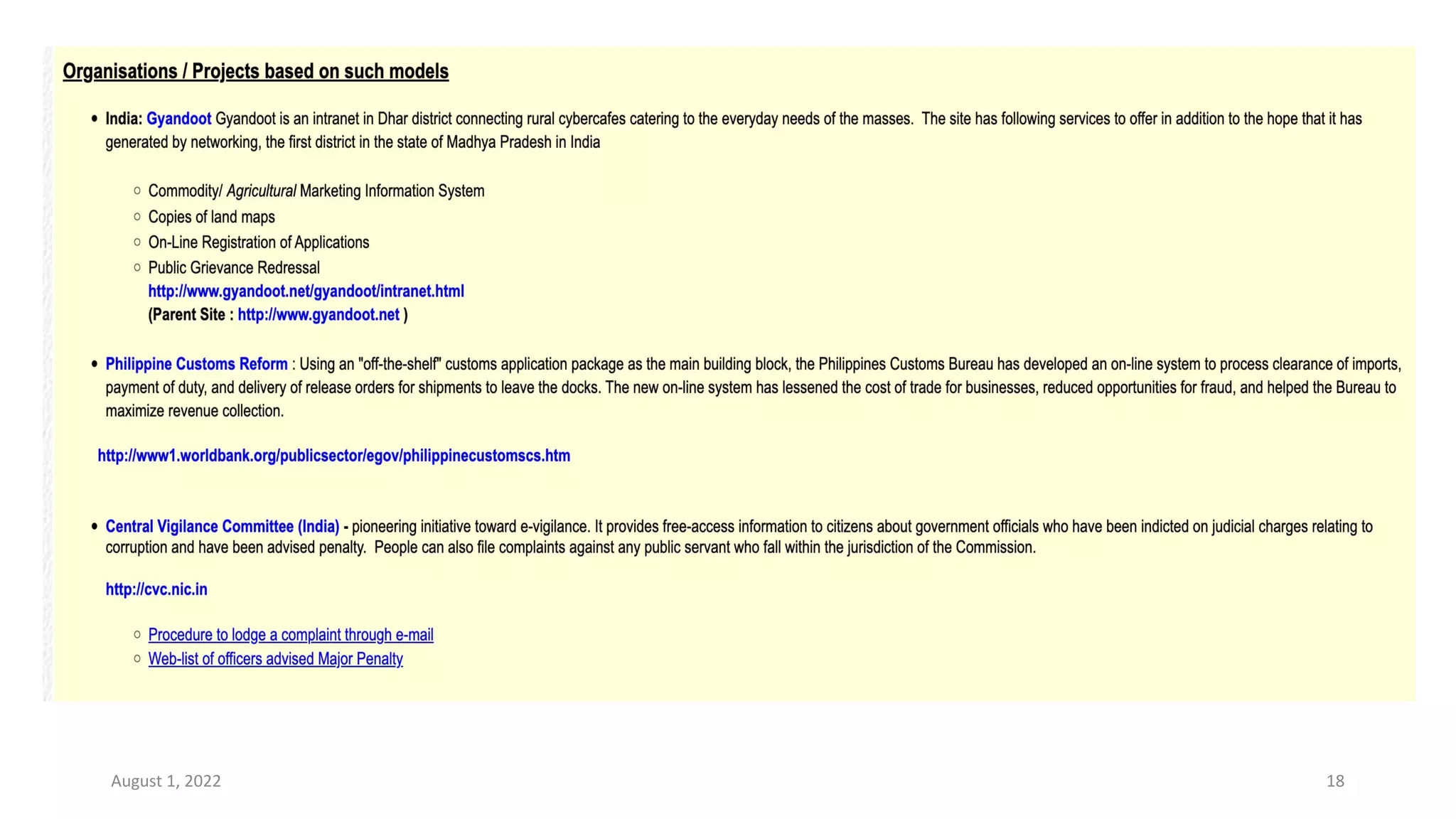
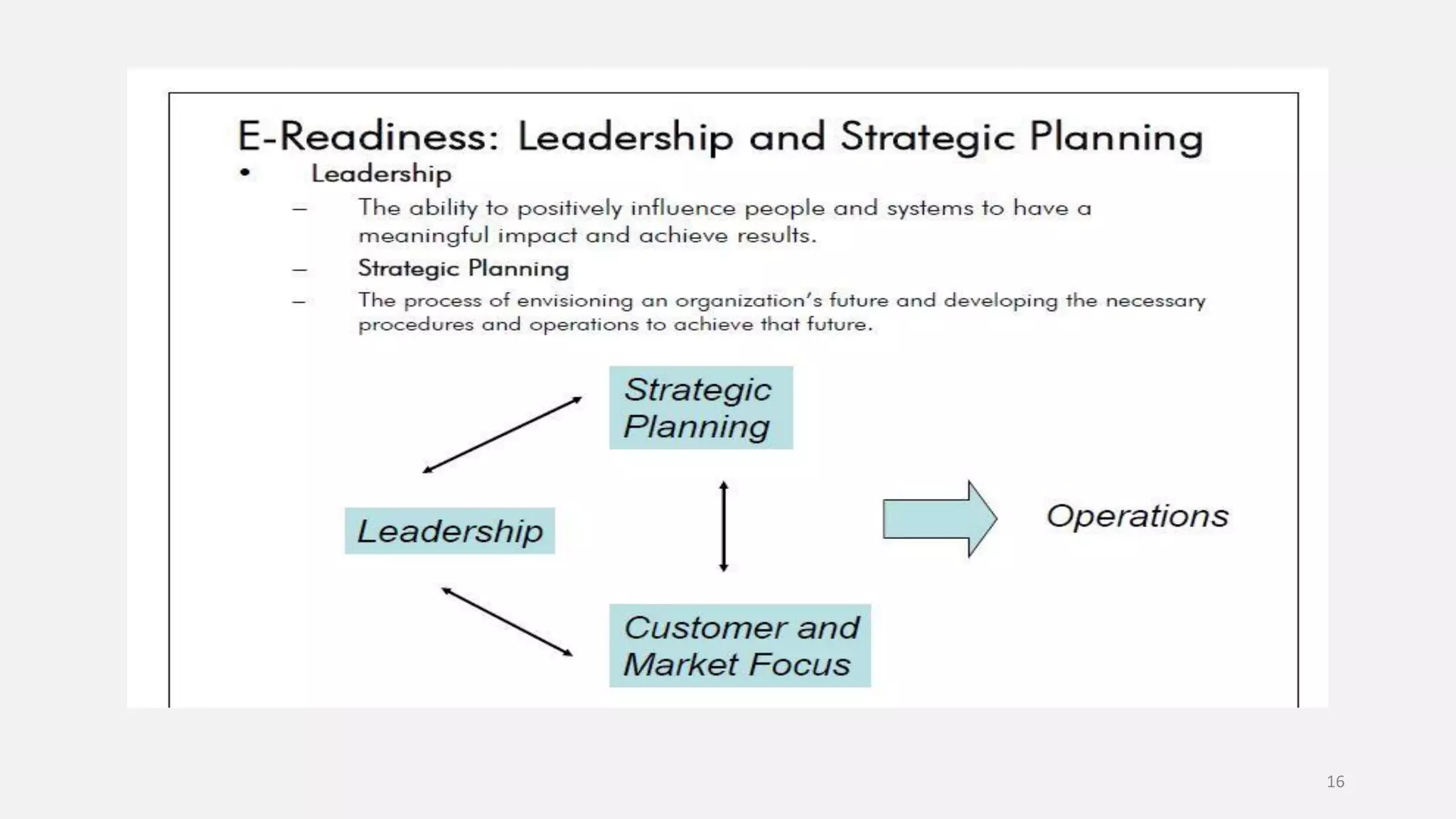
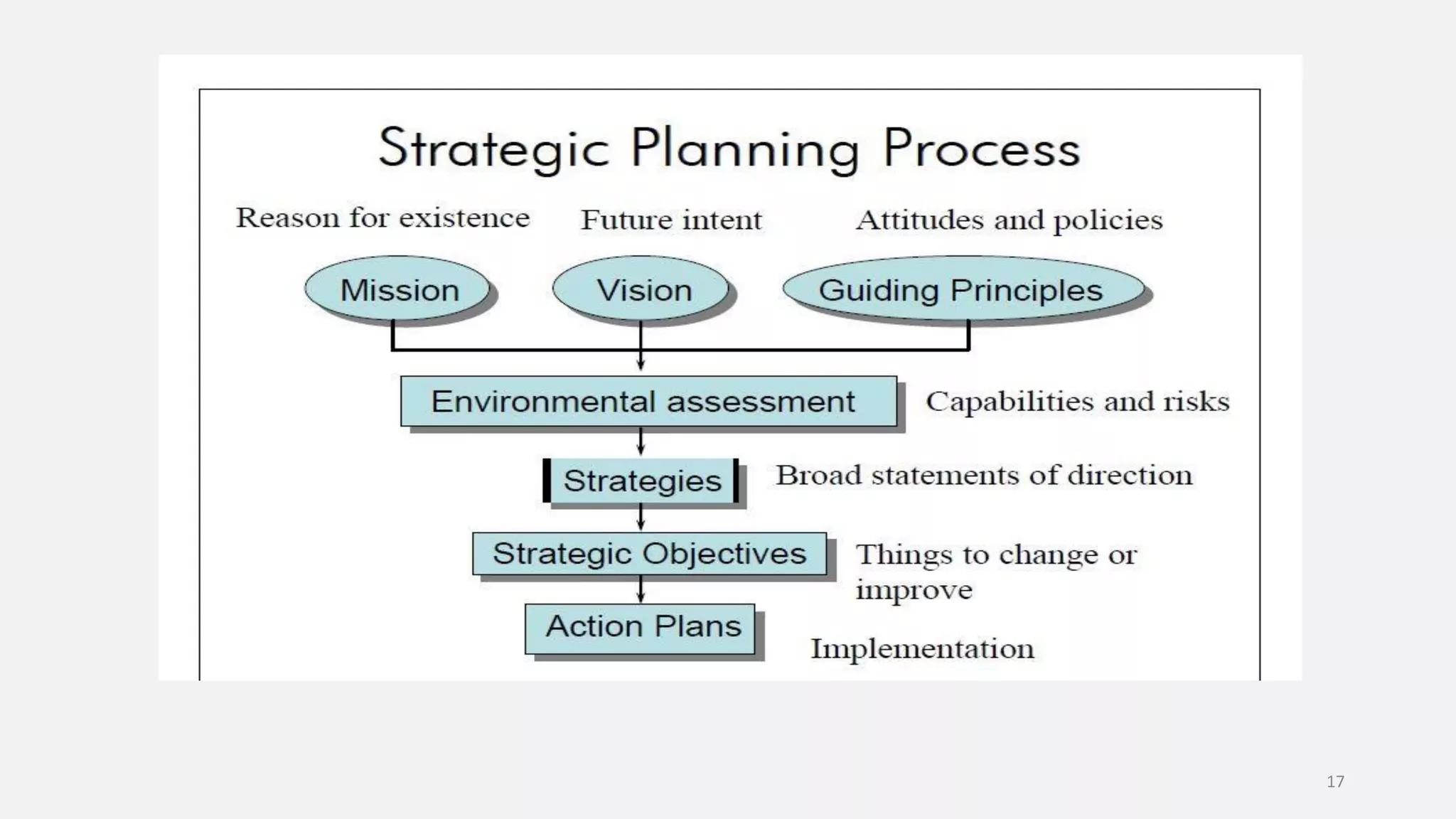
E-governance refers to the use of information and communication technologies by government agencies to provide information and services to the public. The main goals of e-governance are to create a better business environment, strengthen good governance, improve government efficiency and productivity, and improve quality of life. Some key benefits include reduced corruption, increased transparency, convenience for citizens, economic growth, and lower costs. However, e-governance initiatives risk exacerbating the digital divide between those who can and cannot access online services.