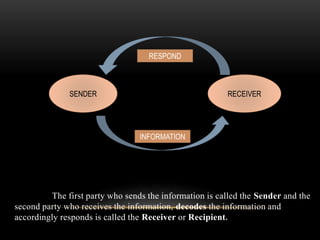
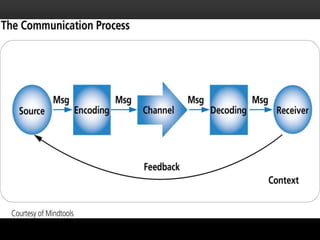
The document discusses effective communication skills. It defines effective communication as communication that produces the intended result. It explains the communication process, which involves a sender, message, encoding, channel, receiver, decoding, feedback, and potential noise. The presentation covers the importance of effective communication in business, such as building trust and improving productivity. It also provides considerations for effective communication, such as clarifying ideas before communicating and examining the true purpose.