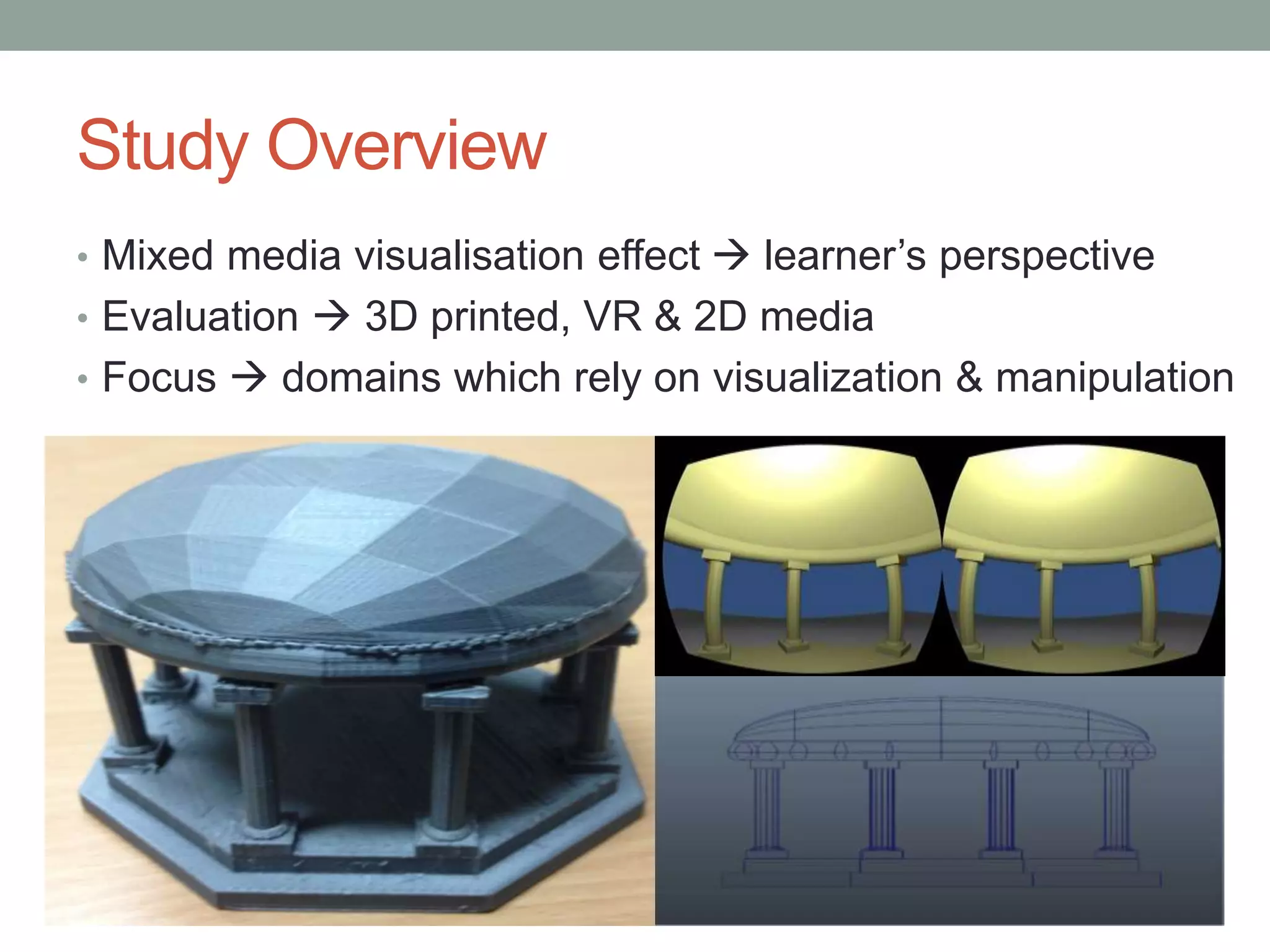
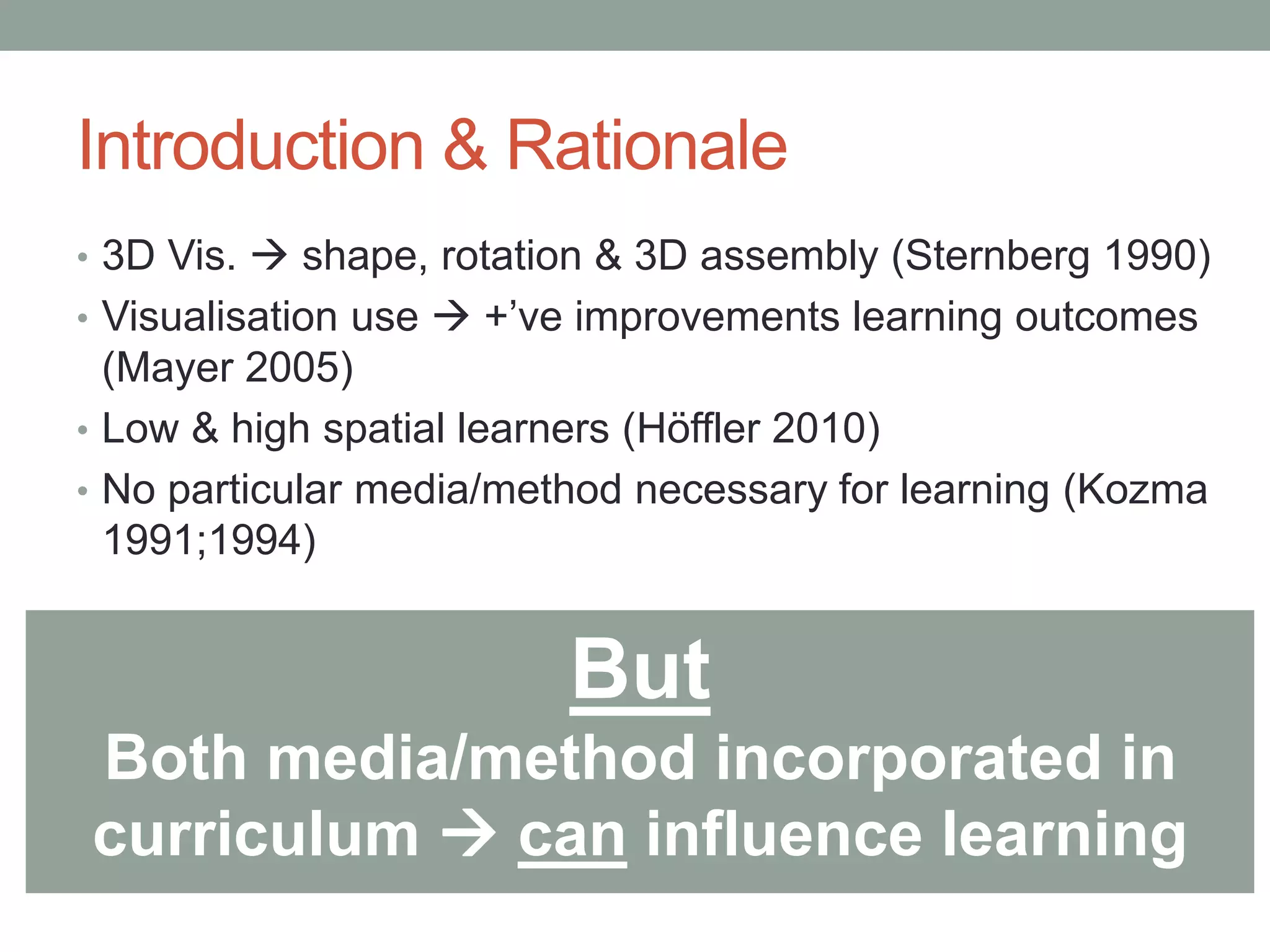
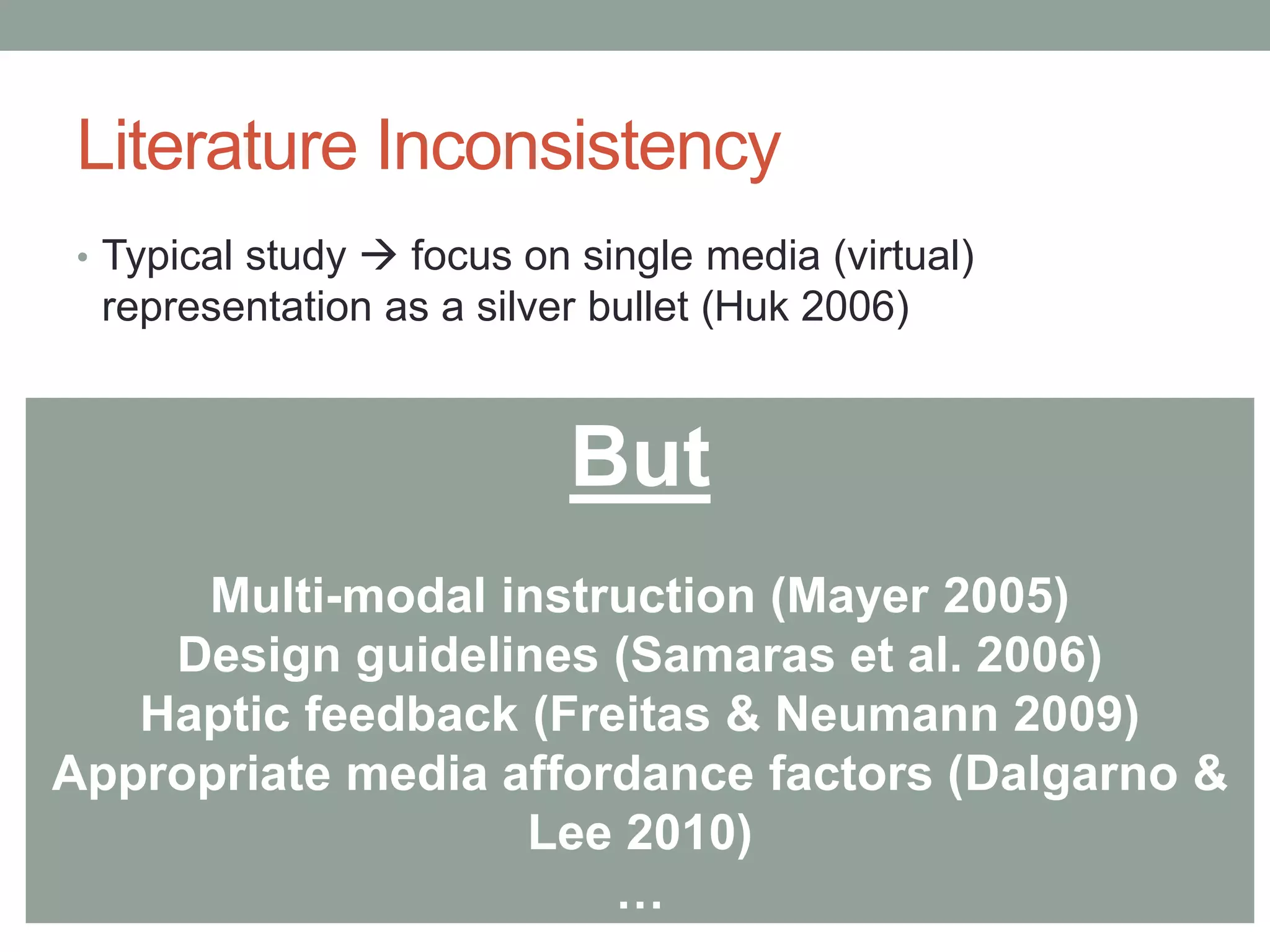
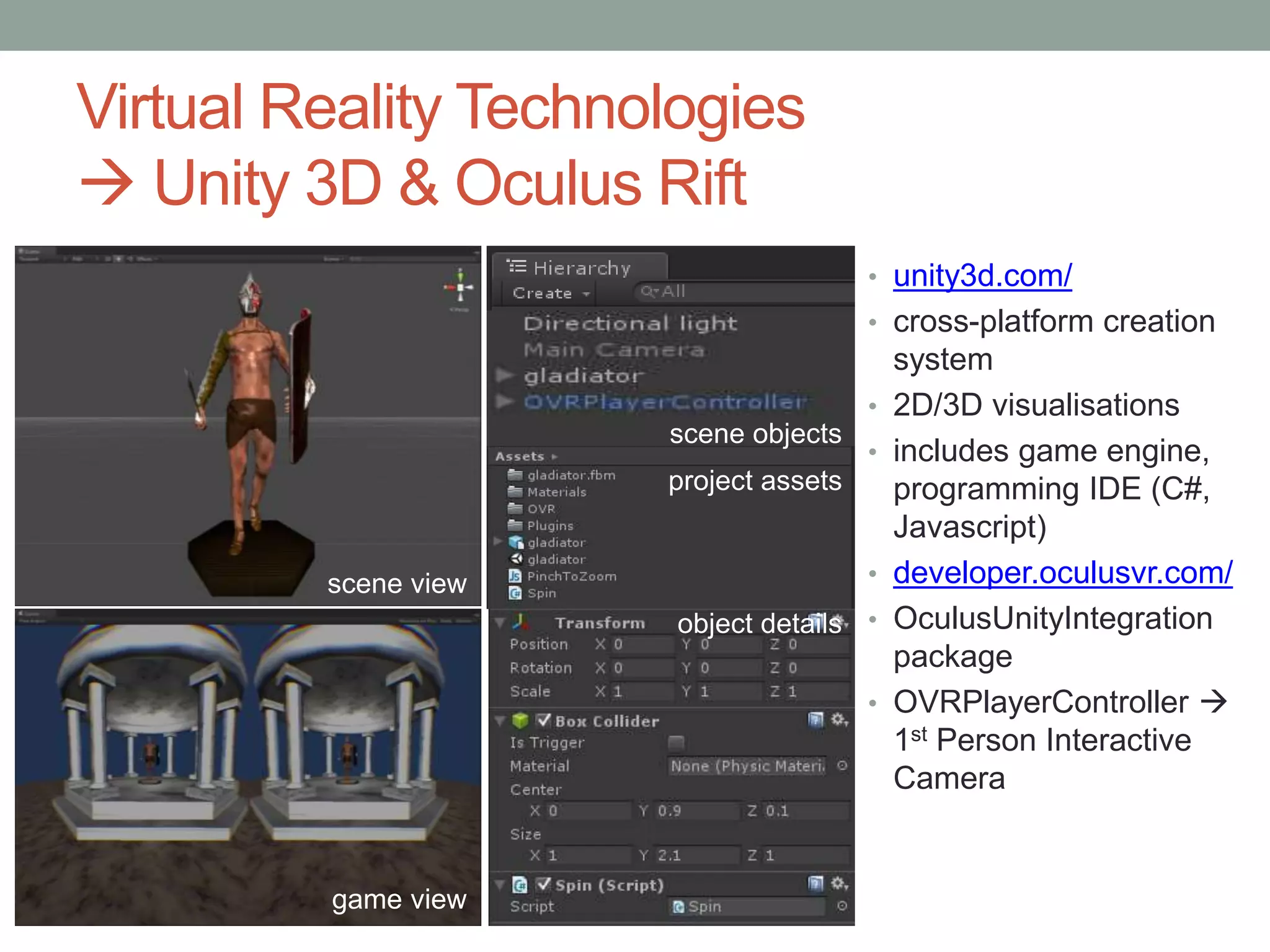
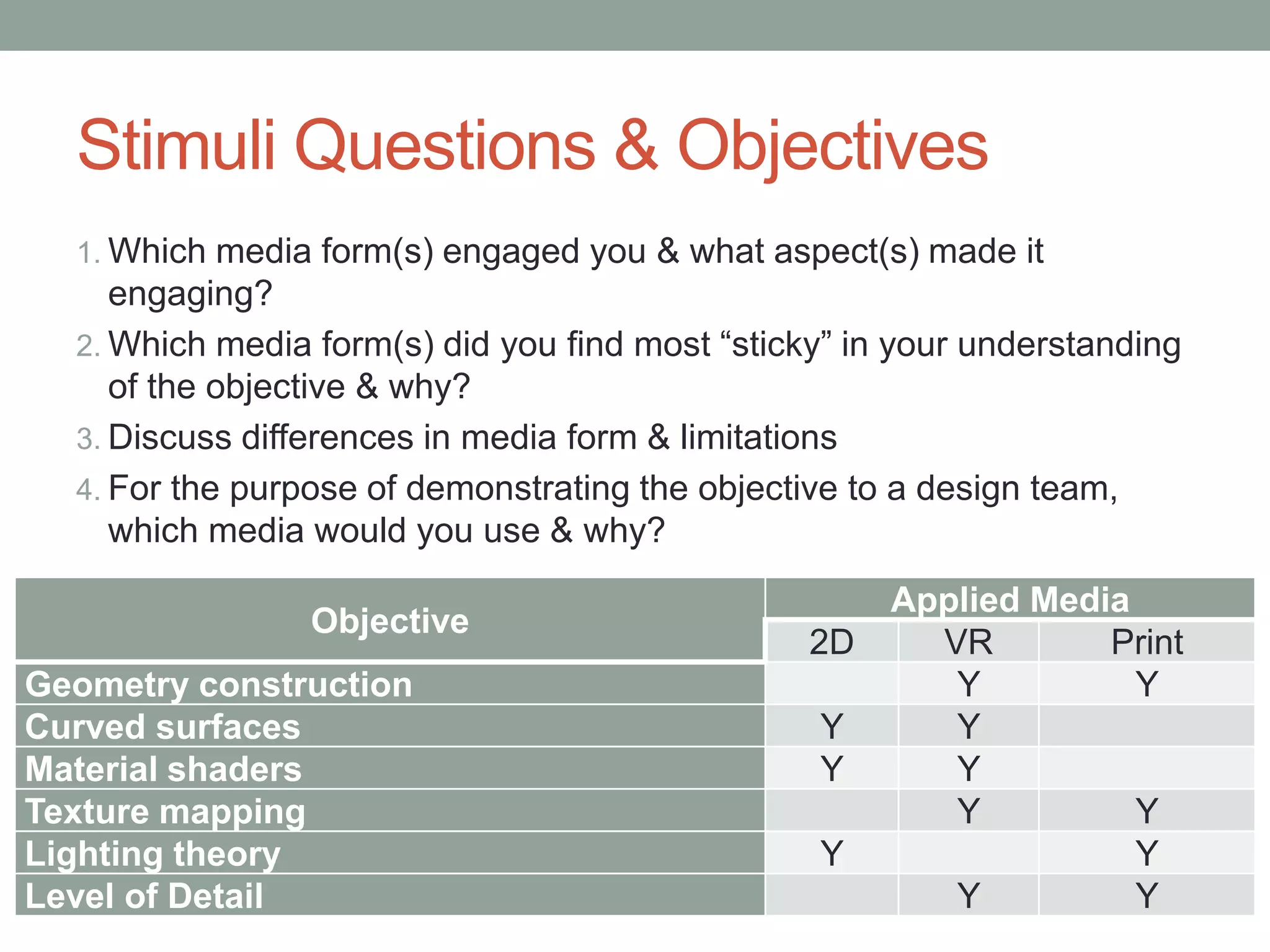
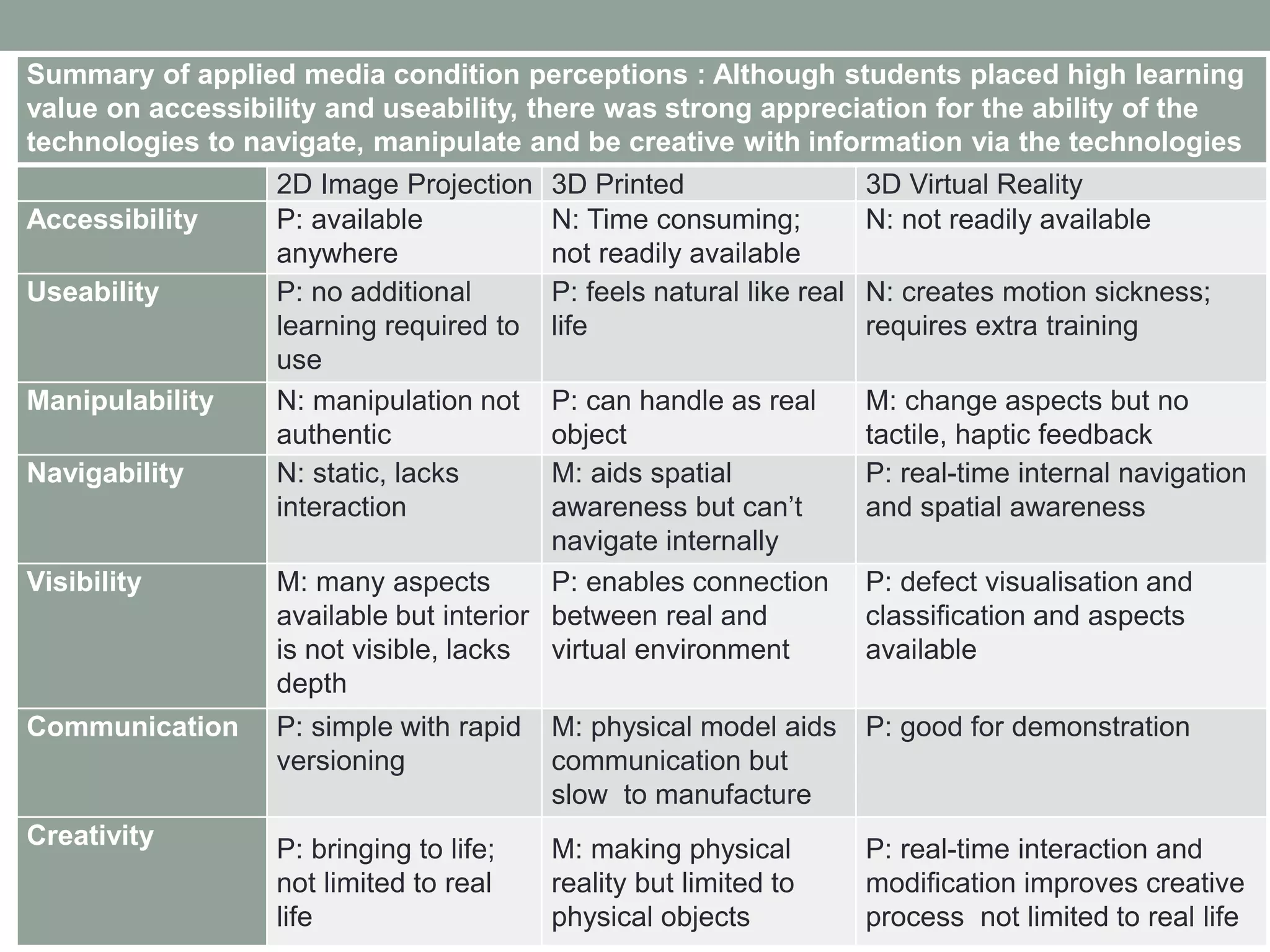
This pilot study evaluates the effects of mixed media visualization on learner perceptions and outcomes in a media and design course. Results indicate that no single visualization technology is preferred by students, as each offers unique strengths, leading to an enhanced blended learning experience over time. The study concludes that while initial technology preferences change, a combination of 2D, 3D printed, and VR media provides comprehensive learning support, suggesting the need for further exploration in diverse contexts.







![Conclusions & Future Work
• Exploratory work discover technologies & lessons for comparative
presentation of material using mixed media
• Extend the study into a wider variety of disciplines
• Correlate student perceptions against student results
• Examine causative relationships inform pedagogy
• Improve VR system increase: manipulation & resolution
• Determine if the technology enables a community of inquiry
• Final Point teaching & learning is NOT about the technology:
“… the real thing that helped me this week was not the visualisation of
the product through physical or virtual aids but the time in observing
them and chatting with others … [the educator] should possibly
consider ""chat"" as one of the options …”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/effectofmixedmediavisualizationonlearnerperceptionsandoutcomes-150106202848-conversion-gate01/75/Effect-of-mixed-media-visualization-on-learner-perceptions-and-outcomes-14-2048.jpg)