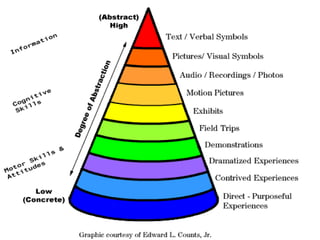
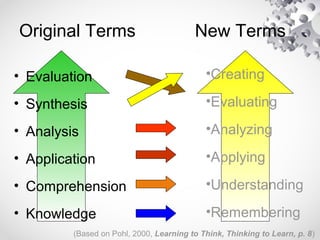
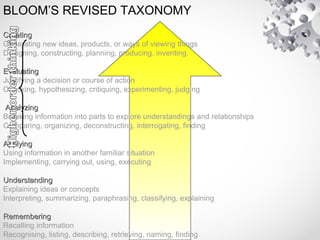
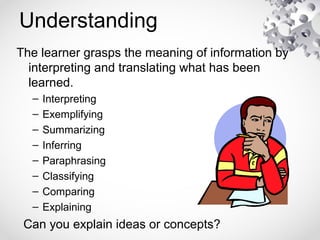
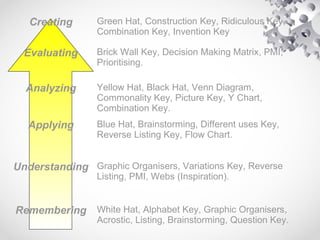
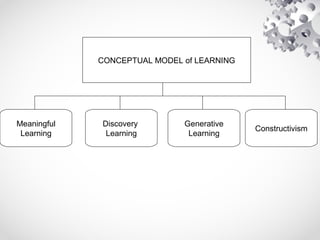
The document contains information about the learner's portfolio in educational technology. It discusses different views of educational technology including the physical, behavioral, and integrated system views. It also defines educational technology according to the Association for Educational Communications and Technology. The document examines technology as both a boon and bane and concludes that technology is necessary and beneficial. It provides examples of how technology can support different roles in learning.