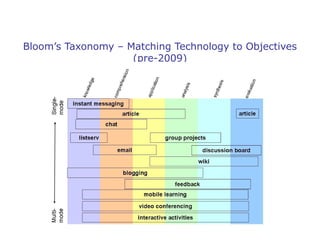
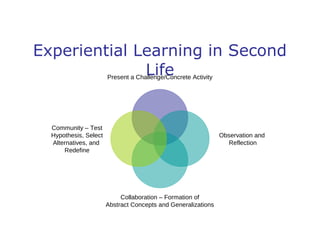
The document discusses the integration of pedagogy and instructional methodologies within virtual environments, particularly in Second Life. It evaluates the effectiveness of these technologies in education based on student and faculty satisfaction, learning effectiveness, and cost-effectiveness while proposing solutions to common challenges such as learning curves and access. Additionally, it explores various learning theories including experiential, transformational, and reflective learning as well as social learning, emphasizing the need for inclusive and engaging learning experiences.