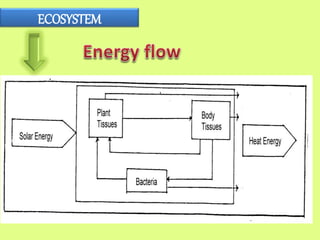
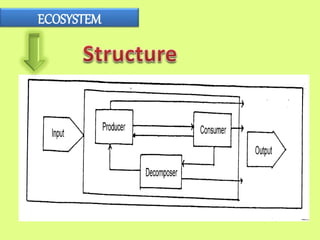
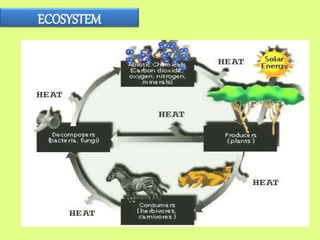
An ecosystem includes all living organisms in a given area, such as plants, animals, and microbes, interacting with each other and their non-living environments like weather, soil and climate. It is defined as a community of living organisms interacting with each other and their non-living surroundings. In an ecosystem, every component depends on every other component, so a change in one factor, such as temperature, can affect other components like what plants grow or how animals adapt. The whole earth contains a series of connected ecosystems often organized into biomes based on similar plant and animal types.