This document discusses revenue concepts in different market structures. It defines revenue, market, and the key market structures - perfect competition, monopolistic competition, and monopoly.
For perfect competition, the document outlines features like many small firms, homogeneous products, free entry and exit. Revenue is constant for each firm as they are price takers.
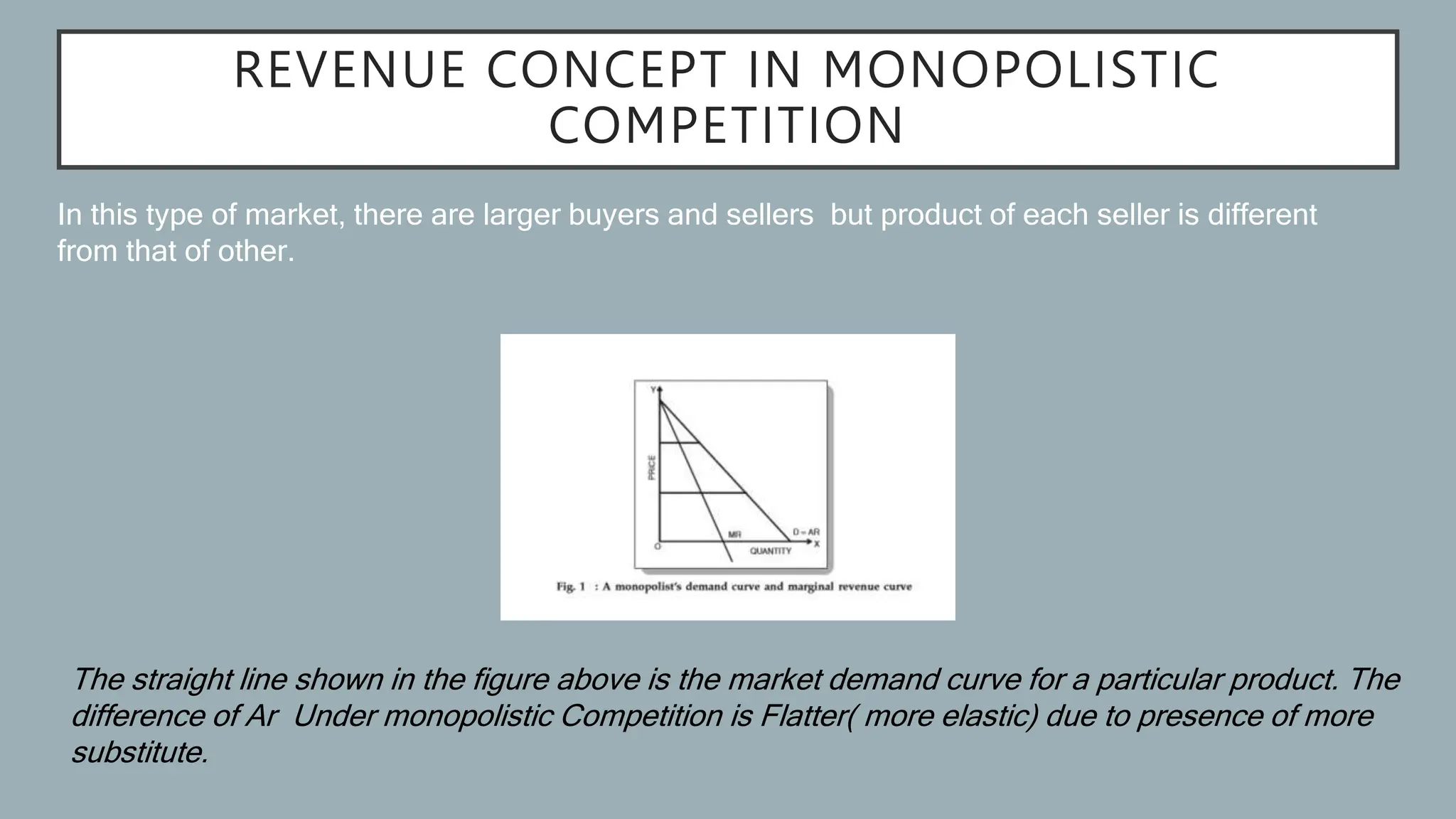
Monopolistic competition has product differentiation and imperfect information. Demand is more elastic.
Monopoly has a single seller, barriers to entry, no close substitutes. The monopolist is a price maker and determines price to maximize profits. Both average and marginal revenue are negatively sloped for a monopoly.