1) The document discusses consumer behavior and equilibrium from a microeconomics perspective. It covers concepts like utility, total utility, marginal utility, indifference curves, budget constraints, and the conditions for consumer equilibrium.
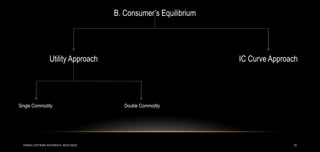
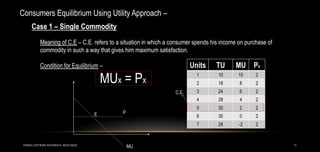
2) Consumer equilibrium is achieved when marginal utility per rupee spent is equal for all goods, or when the budget constraint is tangent to the highest possible indifference curve.
3) Equilibrium is analyzed graphically using indifference curves and budget constraints, as well as through the condition that marginal utility divided by price is equal across goods.