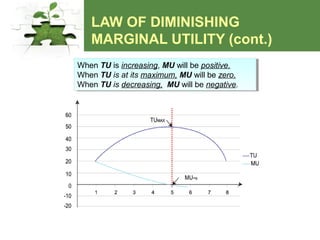
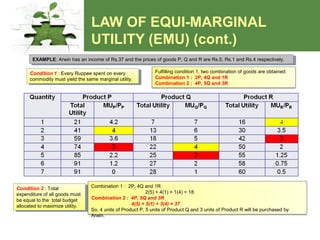
Utility theory examines how consumers derive satisfaction from consuming goods and services. It uses the concepts of total utility, marginal utility, and equi-marginal utility. Total utility is the total satisfaction gained from consumption, while marginal utility refers to the additional satisfaction from consuming one more unit of a good. The law of diminishing marginal utility states that marginal utility decreases with increasing consumption as satisfaction reaches a maximum. The law of equi-marginal utility proposes that consumers maximize satisfaction when the marginal utility per rupee spent is equal across goods, within the constraints of their budget.