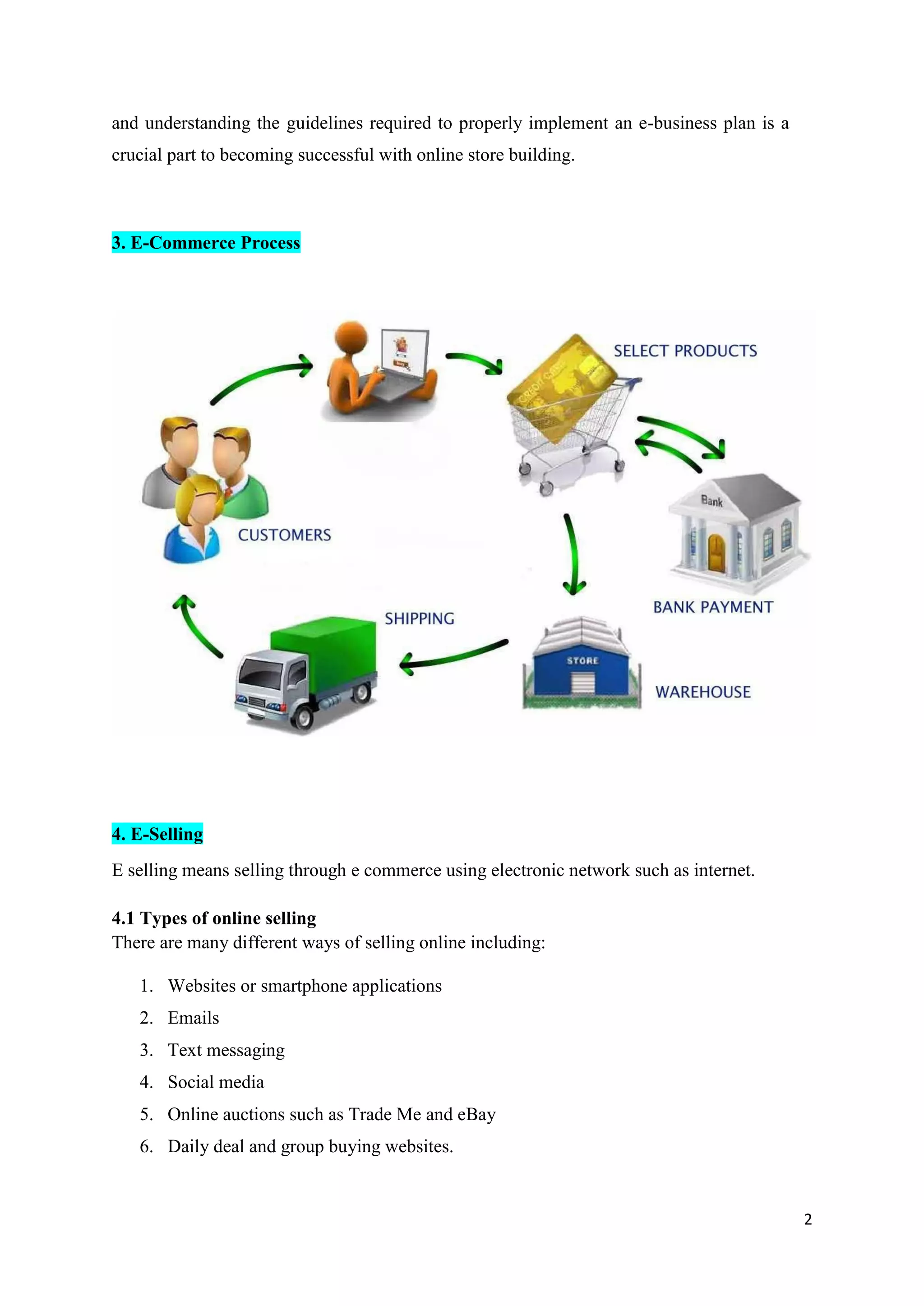
The document outlines the rules, regulations, and guidelines for selling internationally through e-commerce, emphasizing the importance of adhering to these standards for online transactions. It covers various aspects of e-commerce, including the historical context, the process of e-selling, and specific legal requirements that differ by country. Additionally, it highlights the necessity for businesses to implement customer-friendly practices and comply with legal frameworks to foster consumer trust and secure online commerce.