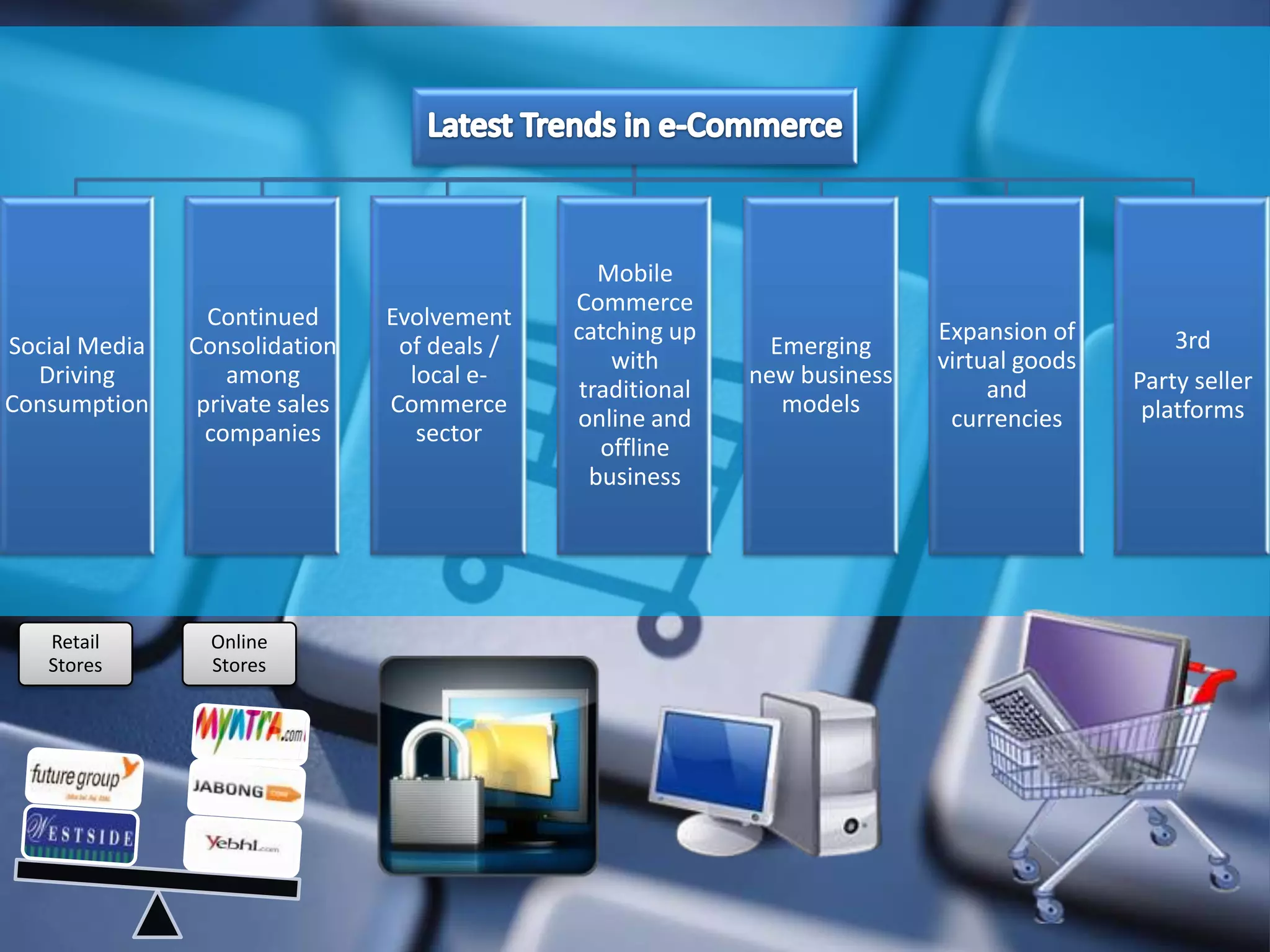
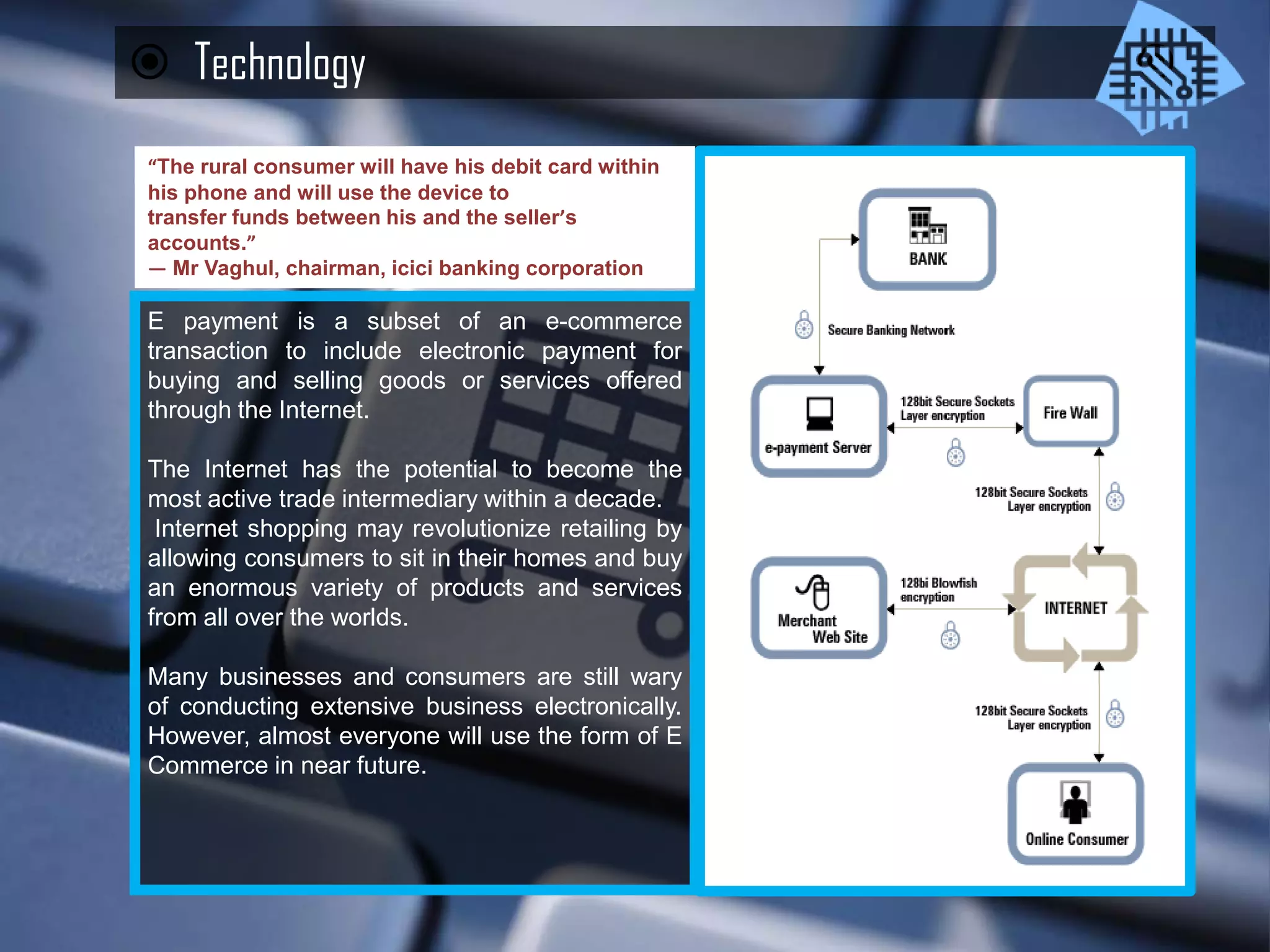
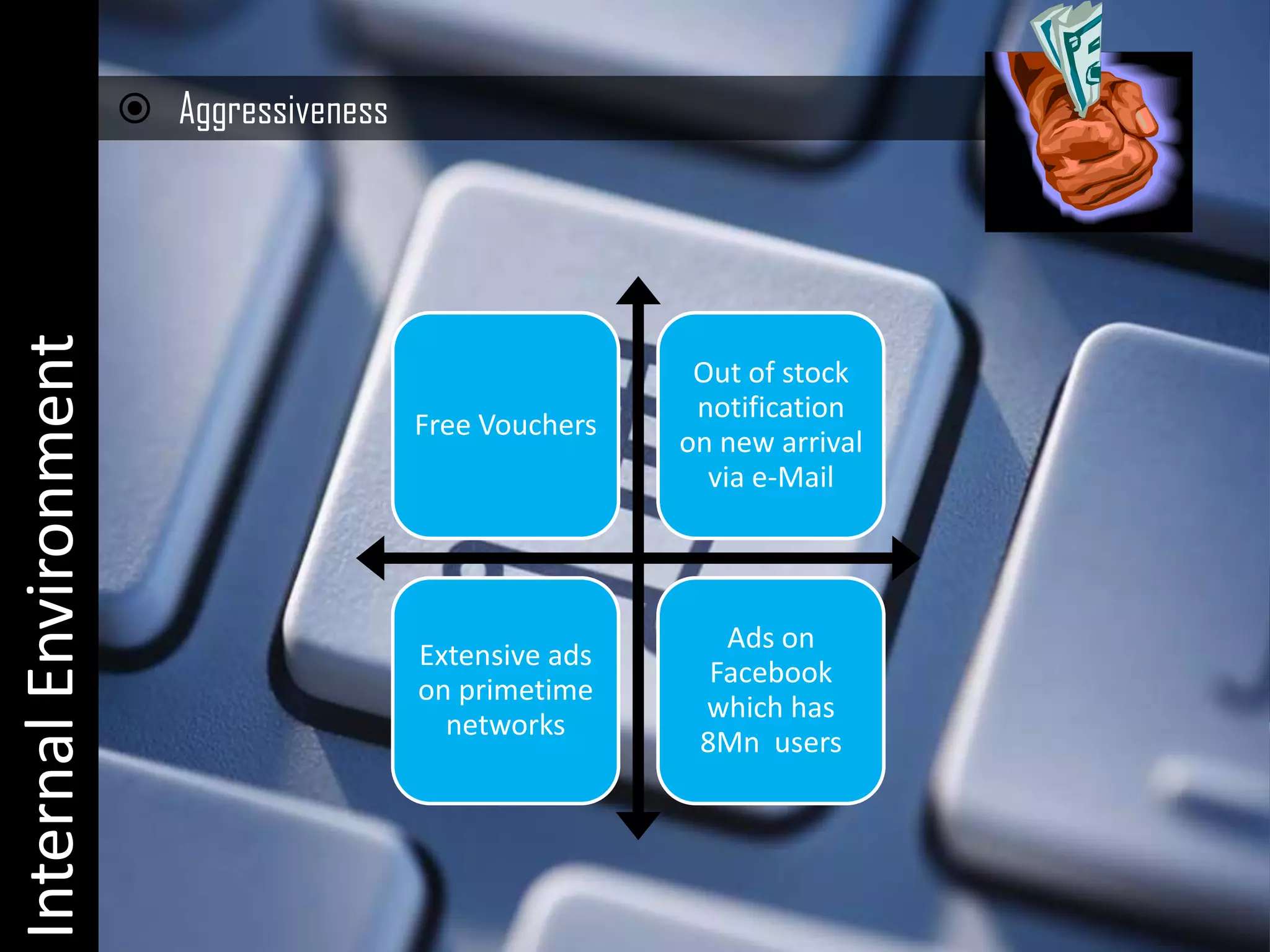
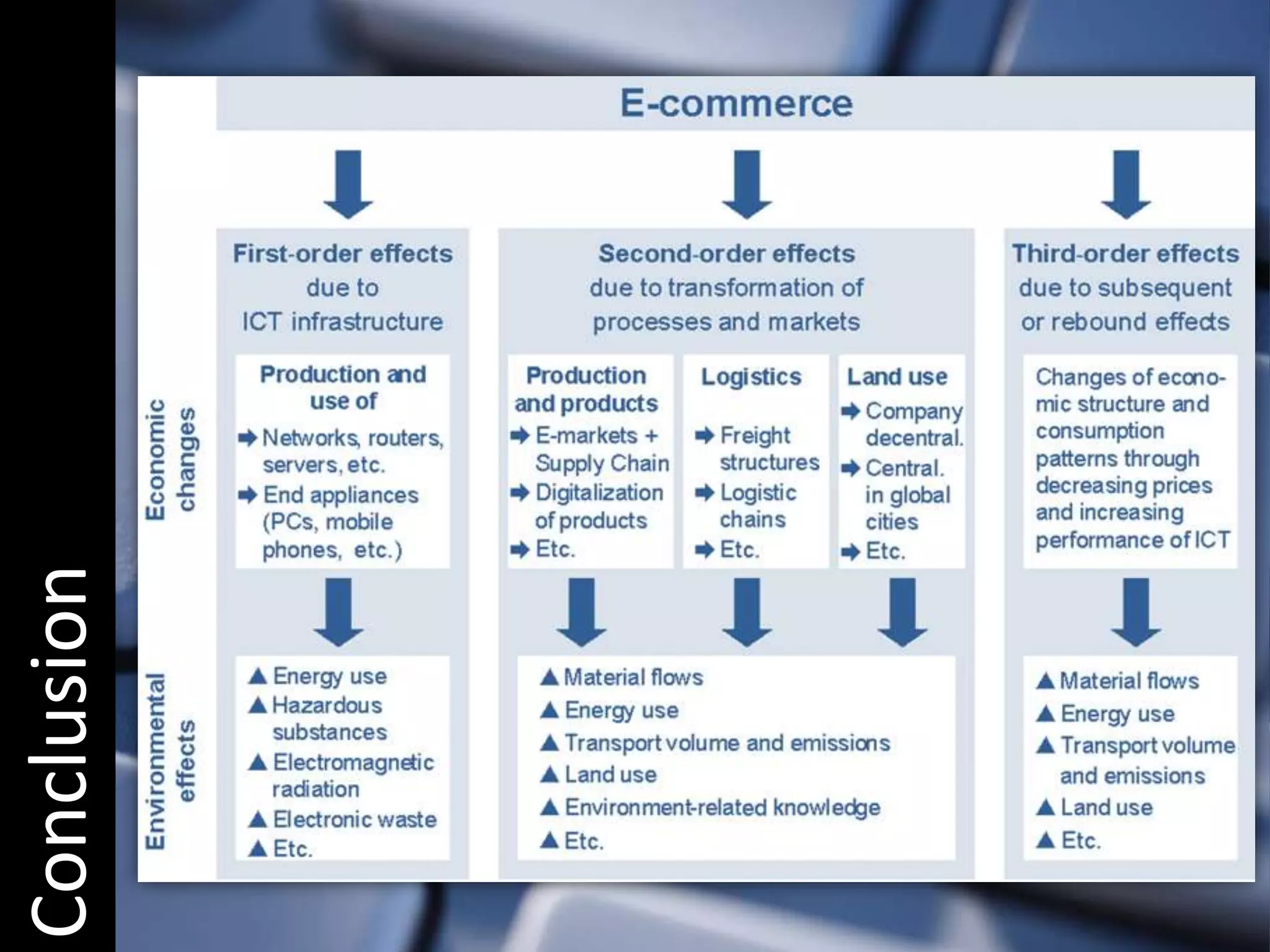
E-commerce encompasses a broad range of electronic transactions including buying, selling, customer service, and inventory management beyond just online shopping. The document discusses the evolution and perspectives of e-commerce, its legal and economic context in India, and the emerging demographic trends that influence consumption patterns. Additionally, it highlights the challenges and advantages for small to medium enterprises in developing countries, emphasizing the importance of technology and awareness for growth in this sector.