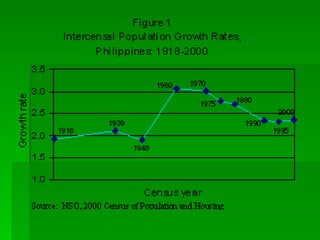
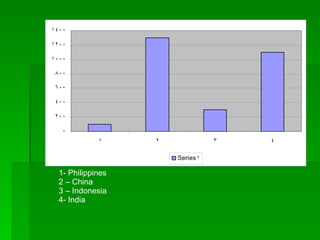
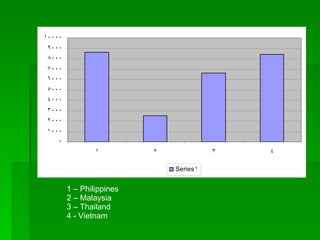
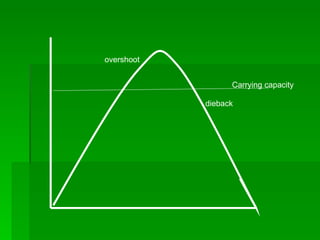
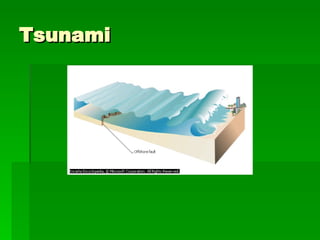
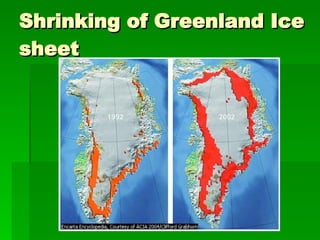
1. Ecology is the study of the relationships between living organisms and their physical environment. This includes factors like light, heat, moisture, nutrients and interactions between different species.
2. An ecosystem is a biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment. Major parts include producers, consumers, decomposers and abiotic (non-living) elements. Inputs include energy, water, nutrients and outputs include food webs and material cycles.
3. A food web shows the transfer of energy between organisms as one species eats another. It involves producers, primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, and decomposers which break down waste. Species also interact through predation, competition, parasitism and coevolution