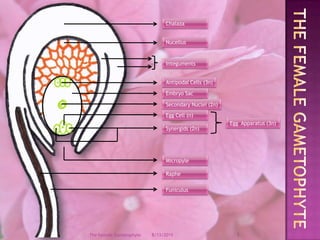
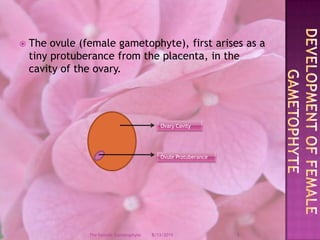
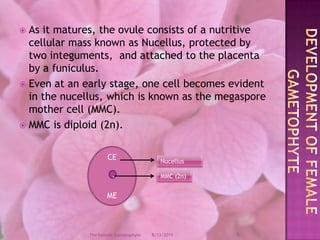
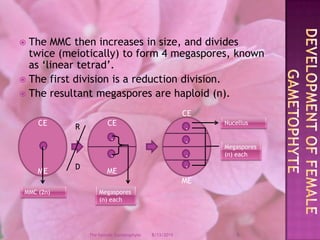
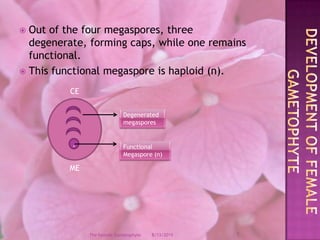
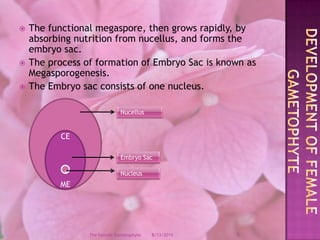
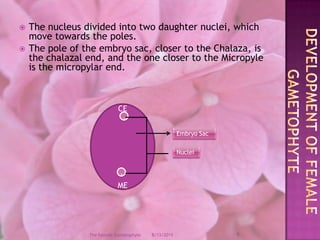
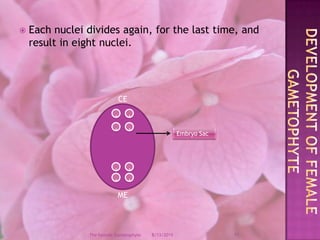
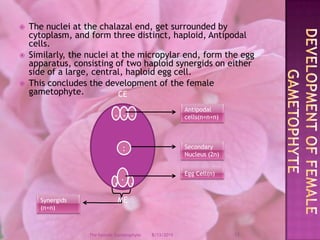
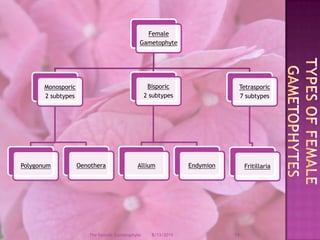
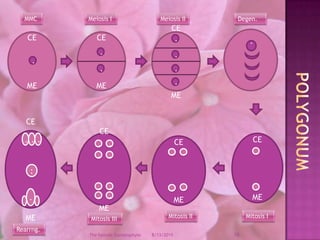
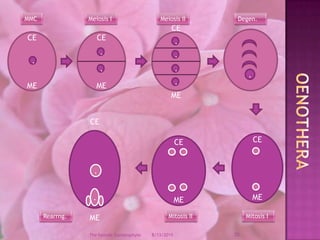
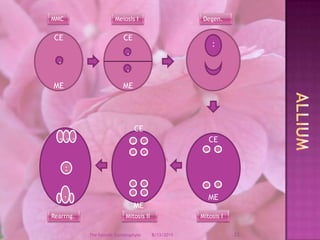
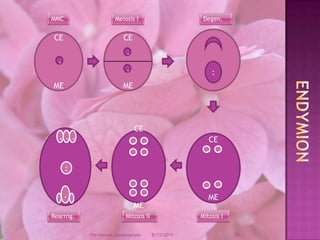
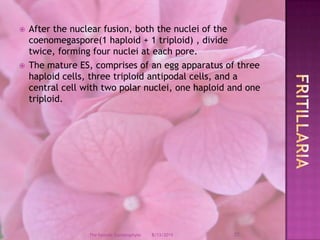
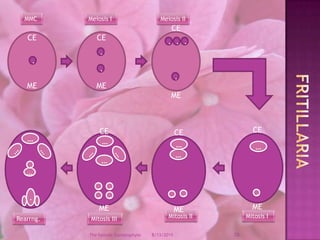
The document provides a comprehensive overview of female gametophyte development, detailing the stages from the initial formation of the ovule to the various types of female gametophytes, including monosporic, bisporic, and tetrasporic classifications. It describes the processes of megasporogenesis and the division of nuclei that lead to the formation of the embryo sac. Each type of female gametophyte is characterized by the genetic composition and number of megaspores involved in the embryo sac's development.