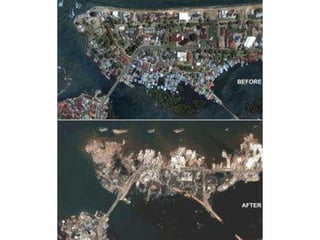
The document discusses ecology, environment, and sustainable development. It defines key terms like ecology, environment, and sustainable development. It then discusses some of the major environmental problems facing humanity, like global warming. Global warming is caused by increased greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane from human activities. This is trapping more heat in the lower atmosphere and causing issues like melting ice caps and changes to climate and habitats worldwide. The document ends by suggesting some individual actions people can take to help address these environmental challenges.