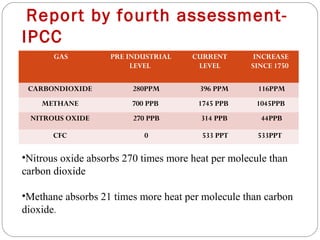
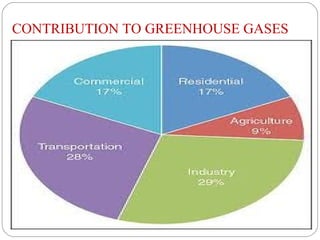
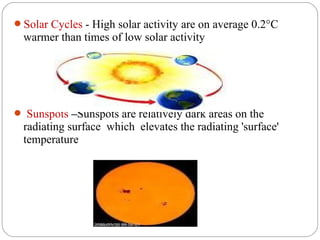
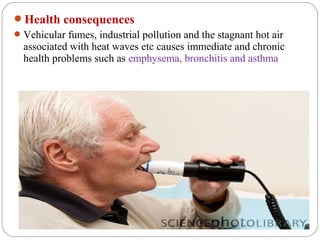
The document discusses global warming, defining it as the average increase in Earth's atmospheric temperature due to greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide trapping heat. It notes global warming can have both natural causes like climate cycles and volcanic eruptions, as well as man-made causes such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and agricultural activities. The impacts of global warming include rising sea levels, stronger hurricanes, droughts, and species extinction. The document provides recommendations for preventing further global warming through individual actions like using renewable energy, driving and flying less, planting trees, and encouraging others.