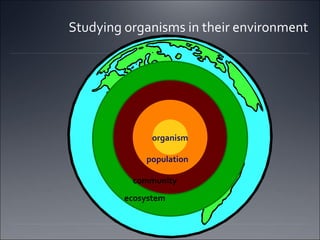
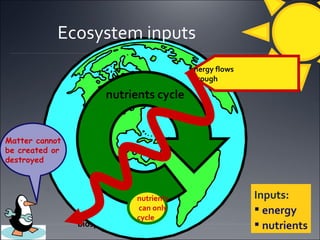
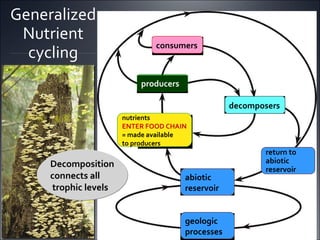
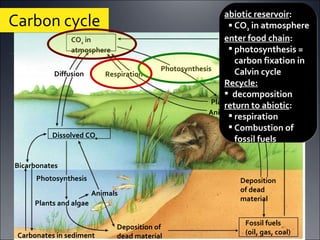
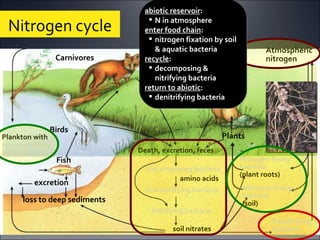
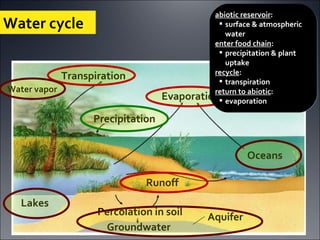
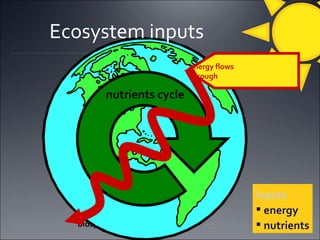
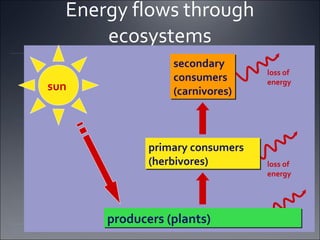
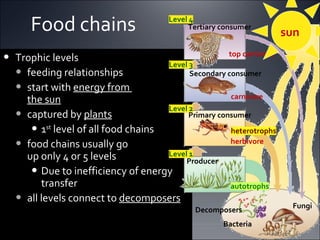
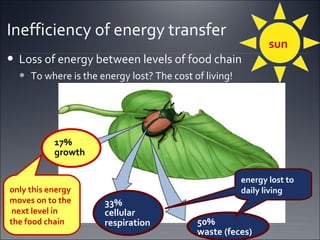
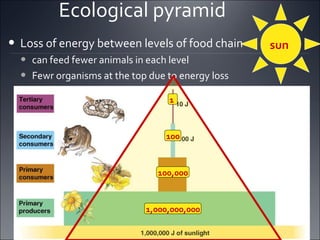
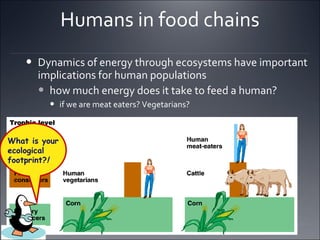
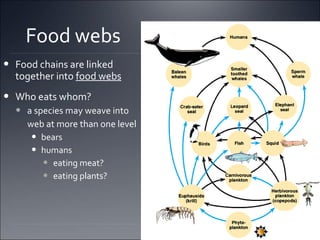
Ecosystems involve the interactions between organisms and their environment. Energy from the sun flows through ecosystems via producers, primary and secondary consumers, and decomposers in food chains and webs. Nutrients also cycle through ecosystems, entering via inputs like sunlight and geological processes and returning to non-living reservoirs through decomposition. Key nutrient cycles include carbon, nitrogen, and water. Ecosystems are self-sustaining systems that transform energy and process matter according to the laws of physics.