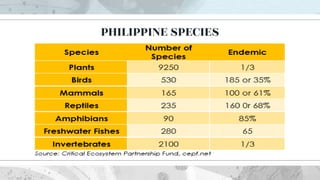
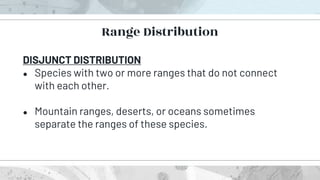
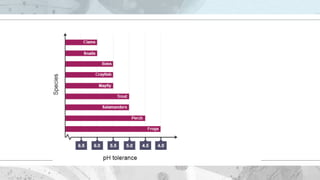
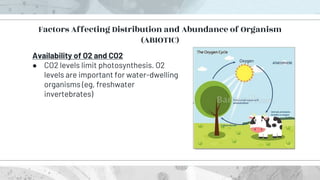
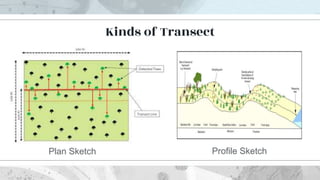
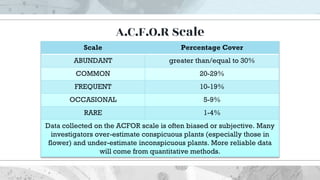
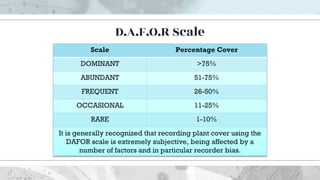
This document discusses the distribution and abundance of organisms. It defines different types of distributions like cosmopolitan, endemic, disjunct, clumped, regular, and random. Abundance refers to the number of individuals in an area and can be measured using quadrats, transects, pitfall traps, and capture-recapture methods. Both biotic and abiotic factors affect distribution and abundance, such as temperature, moisture, pH, food availability, and new predators or pathogens. Measurement scales include semi-quantitative ratings like ACFOR.