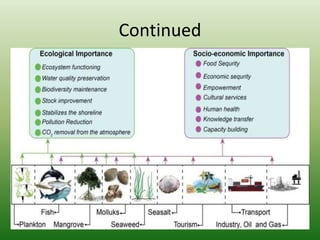
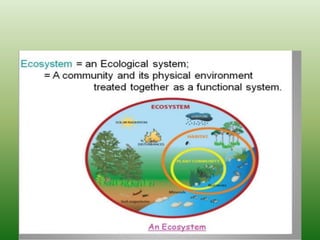
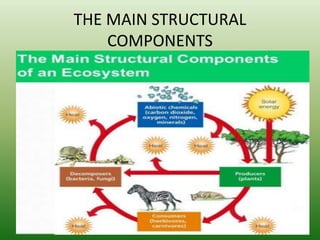
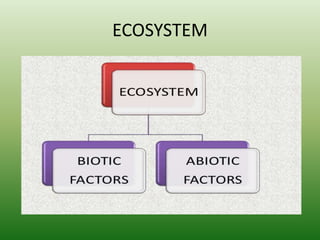
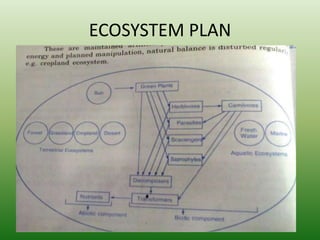
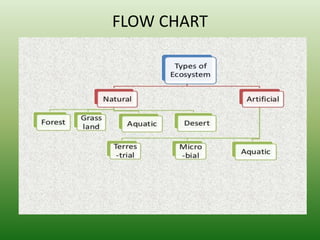
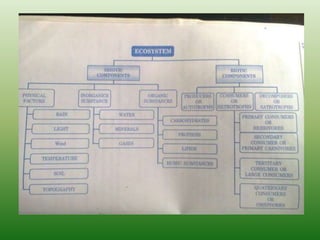
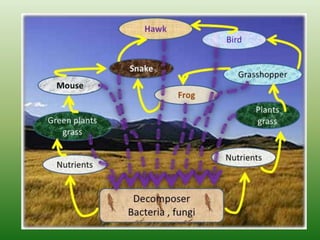
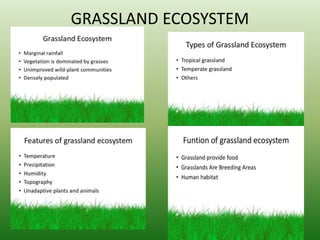
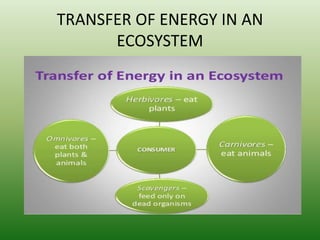
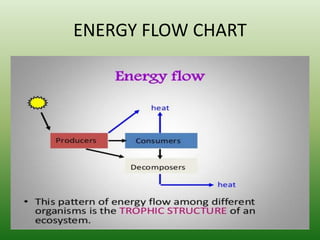
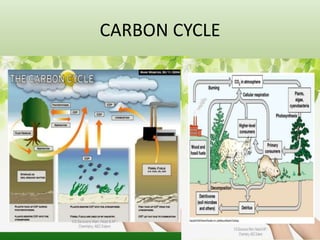
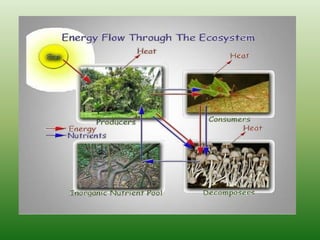
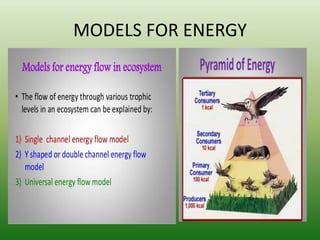
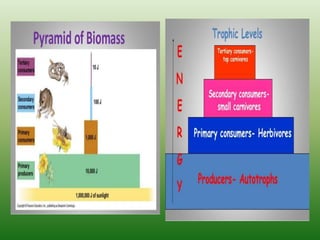
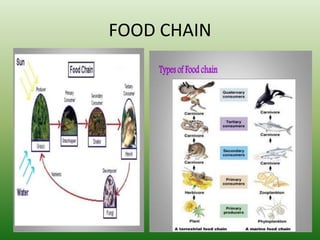
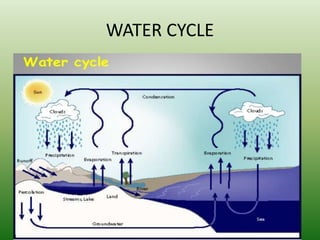
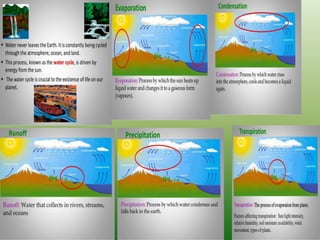
The document defines an ecosystem as a community of living organisms that interact with each other and their physical environment. It describes the key components of an ecosystem as the biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors. Some examples of ecosystem types are given such as forests, deserts, grasslands and aquatic ecosystems. The functions of ecosystems are also outlined, including the cycling of nutrients and flow of energy. Global threats to ecosystem viability are mentioned. In conclusion, the document provides an overview of ecosystems, their structures, functions and threats.