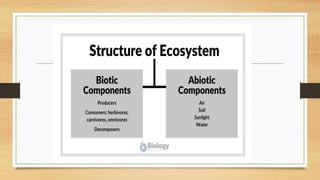
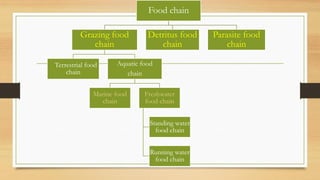
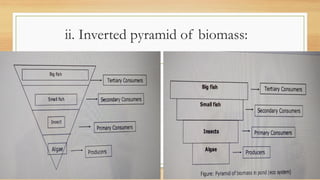
This document provides an overview of different ecosystem types and their structures and functions. It begins by defining ecology and ecosystems. The key components of an ecosystem include biotic factors like producers, consumers, and decomposers, as well as abiotic factors like climate, soil and water. Ecosystems function through food chains, food webs, and nutrient cycling. Major ecosystem types discussed include forests, grasslands, deserts, freshwater systems like ponds and rivers, and marine systems like oceans. Each ecosystem has unique structural features and inhabitants that have adapted to the environmental conditions.