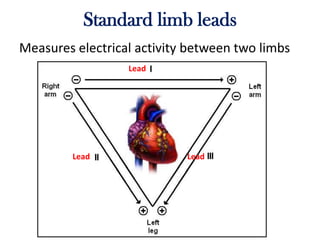
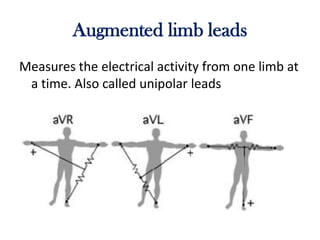
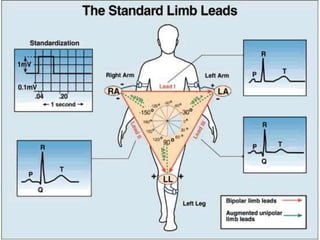
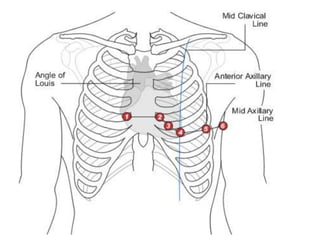
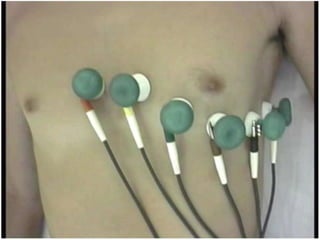
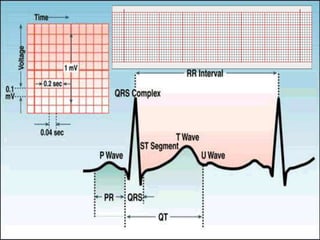
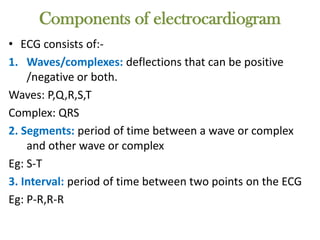
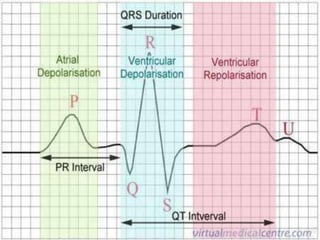
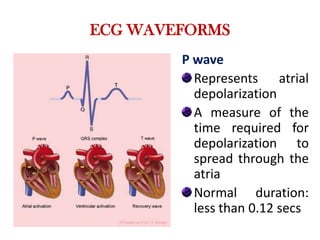
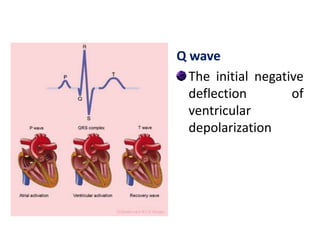
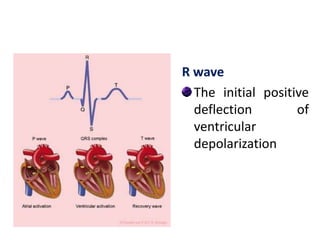
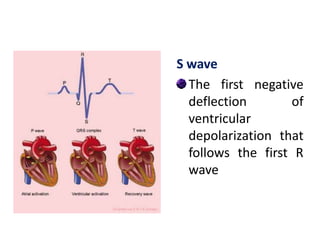
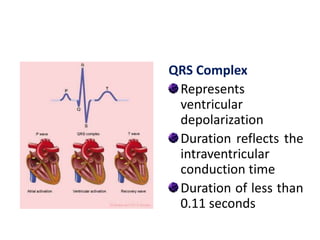
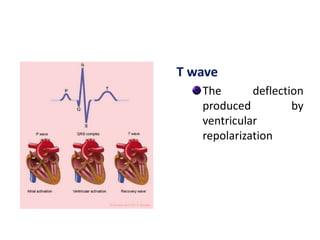
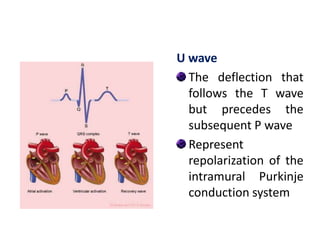
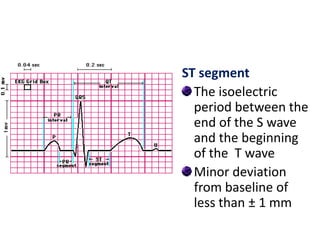
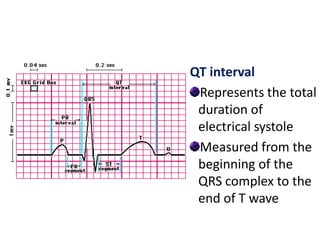
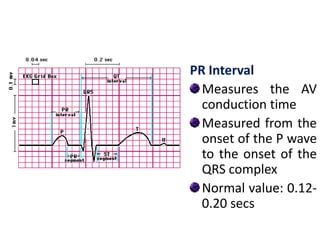
The electrocardiogram (ECG) measures the electrical activity of the heart. There are 12 conventional ECG leads that measure the heart from different angles. The ECG uses electrodes placed on the limbs and chest to record the heart's electrical signals as waveforms on graph paper over time, showing deflections like the P, Q, R, S, and T waves. The ECG provides information about heart rate, rhythms, and time intervals to evaluate for conditions like arrhythmias or conduction delays.