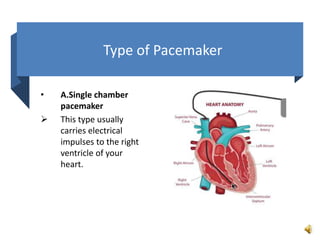
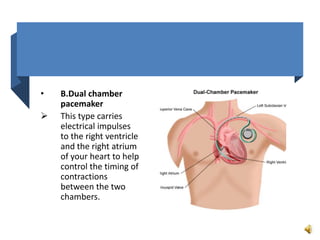
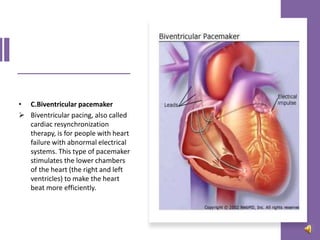
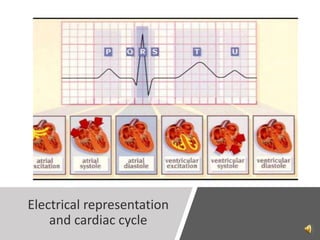
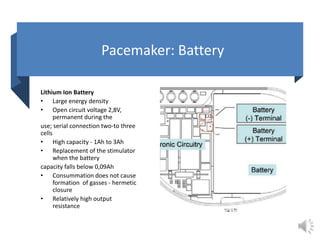
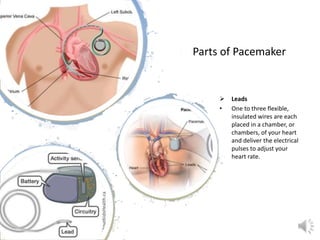
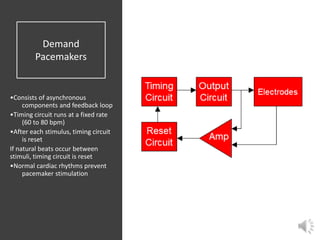
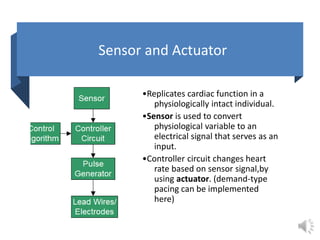
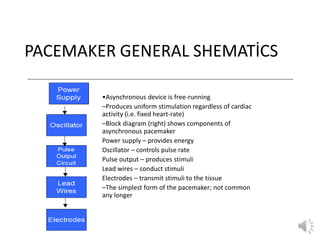
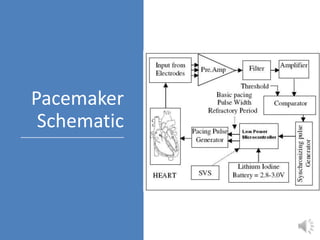
A pacemaker is a small device implanted in the chest or abdomen to help control abnormal heart rhythms and regulate a slow heartbeat. There are several types of pacemakers including single chamber, dual chamber, and biventricular pacemakers. A pacemaker consists of a pulse generator housed in a metal container that contains a battery and electrical circuitry. Leads transmit electrical pulses from the generator to the heart. Pacemakers are implanted via a minor incision and procedure to treat various heart conditions such as bradycardia or heart block. Pacemakers provide benefits of regulating heart rate but also risks such as infection or sensitivity. New pacemaker technologies continue to be developed including leadless pacemakers and apps to monitor devices.