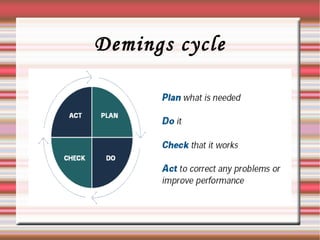
This document outlines eight quality management gurus: Deming, Juran, Crosby, Feigenbaum, Ishikawa, Garvin, Shingo, and Taguchi. It provides brief biographies of each guru, highlighting their major contributions and ideas related to quality management such as statistical process control, quality costs, quality circles, robust design, and total quality management. The document also discusses concepts like the Ishikawa diagram, poka-yoke, single-minute exchange of dies, and off-line quality control.