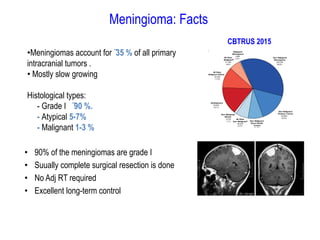
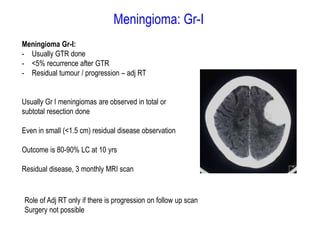
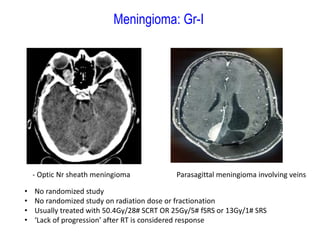
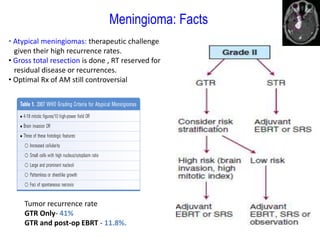
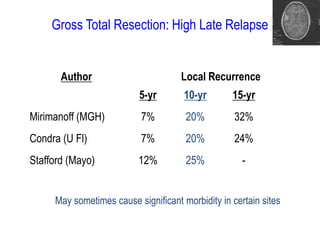
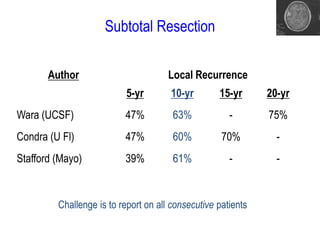
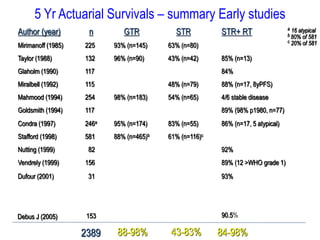
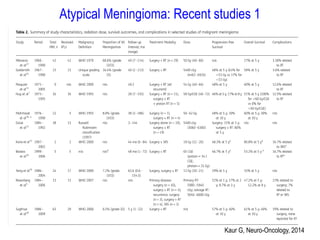
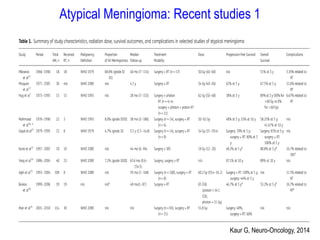
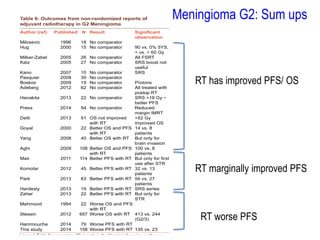
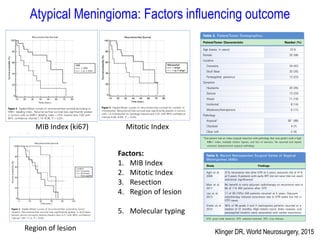
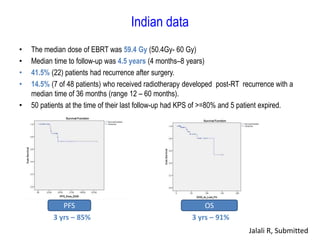
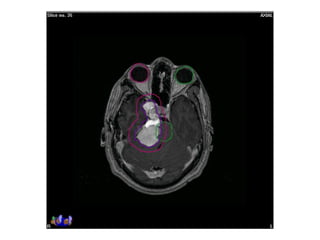
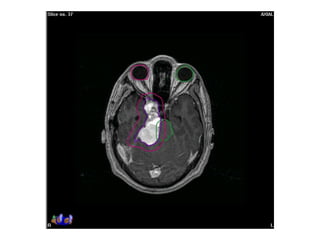
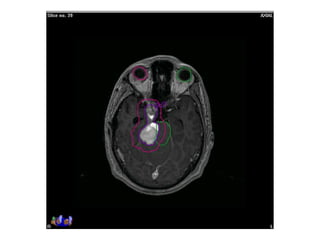
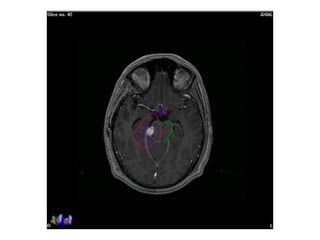
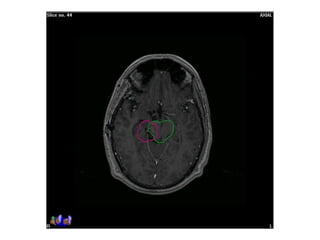
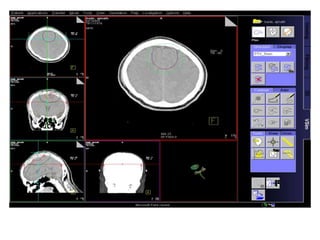
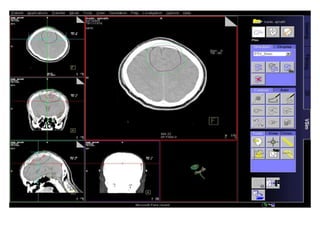
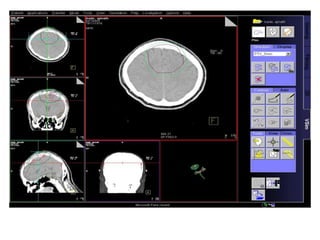
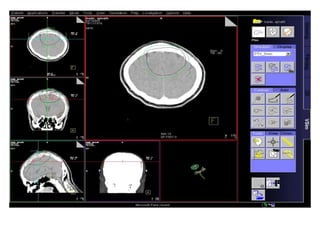
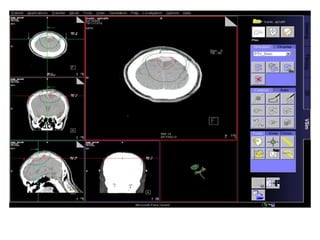
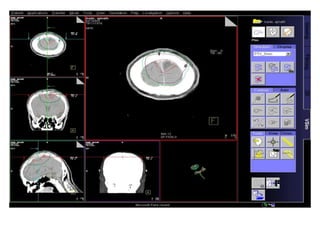
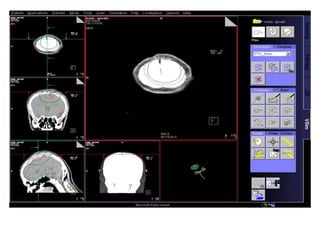
Meningiomas account for approximately 35% of primary intracranial tumors, with about 90% being grade I, which typically requires complete surgical resection without the need for adjuvant radiation therapy (RT). Atypical and anaplastic meningiomas present a therapeutic challenge due to high recurrence rates, often necessitating adjuvant RT following surgery. Treatment strategies, including the use of stereotactic radiosurgery for small volume disease, are evolving, but the optimal approach remains controversial, especially for higher grade tumors.