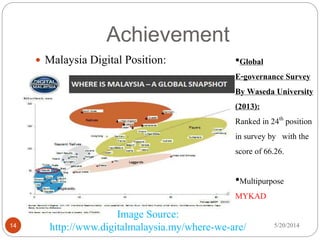
Malaysia initiated e-governance in 1996 through the Multimedia Super Corridor to modernize public administration. Major e-governance projects included the myGovernment portal, HRMIS, GOE, electronic procurement, and e-Services. These provided online government information and transactional services to citizens. Key challenges included integrating legacy systems and ensuring privacy and security as services moved online. Malaysia ranked 24th globally for e-governance in a 2013 UN survey.