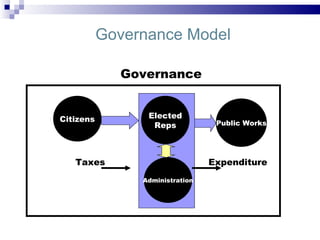
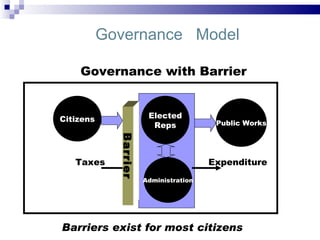
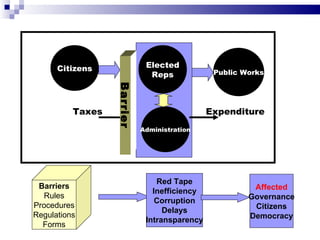
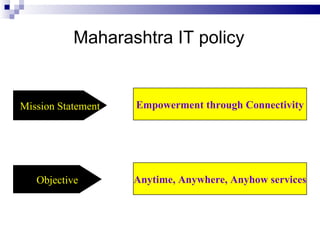
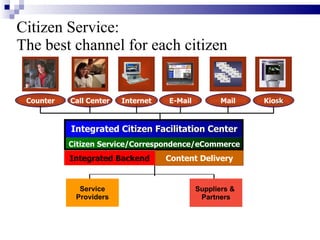
E-governance through information and communication technologies can help drive economic growth by reducing barriers to good governance, expanding citizen participation, and strengthening democracy. It seeks to achieve efficient, transparent governance through technology optimization of services, participation, and relationships. Successful e-governance requires political will, appropriate cyber laws, business process reengineering, staff involvement, and public-private partnerships to reap benefits like access to information, reduced infrastructure needs, and allowing developing countries to leapfrog stages of development. Maharashtra's e-governance policy aims to empower citizens anytime, anywhere through connectivity and reengineering processes rather than just automating existing systems.